Integrated waste management for plastic recycling involves collecting, sorting, cleaning, processing, and reusing plastic waste to create new products.
It’s a comprehensive approach that aims to reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste while promoting resource conservation and sustainability.
integrated waste management (plastic recycling) working model using conveyor belt, screen conveyor, floating tank, friction washer, dewatering and shredder to make new plastic product by recycling
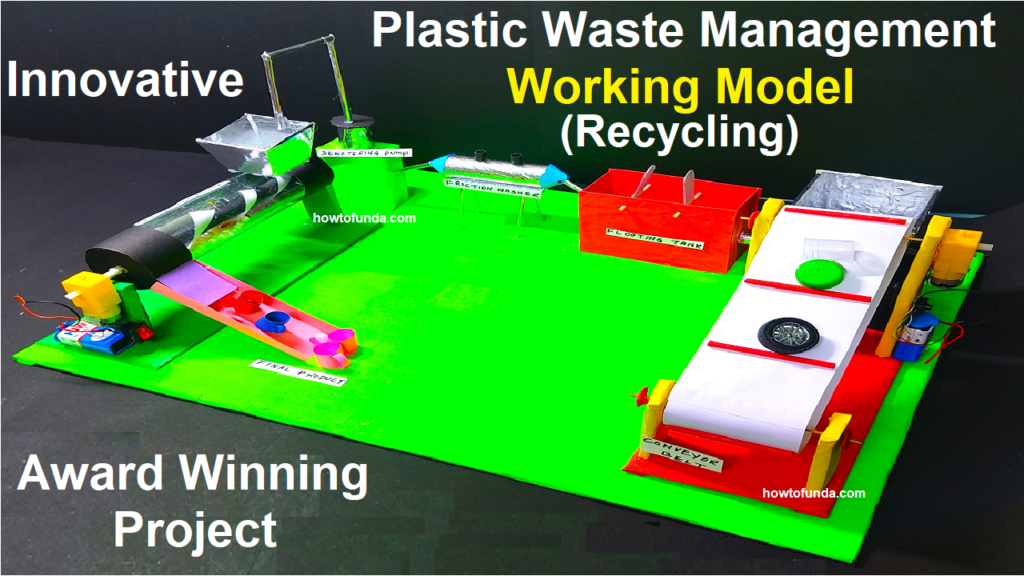
Designing an integrated waste management system for plastic recycling using the components you’ve mentioned is a great initiative. Here’s a step-by-step working model for such a system:
1. Collection and Sorting: Collect plastic waste from various sources and sort them based on their type and quality. This can be done manually or with the help of automated sorting machines.
2. Conveyor Belt 1: Place the sorted plastic waste on the first conveyor belt, which will carry the plastic items to the next stage.
3. Screen Conveyor: The screen conveyor consists of a series of screens with different mesh sizes. As the plastic waste moves along the conveyor, the screens separate it based on size. This helps remove larger debris and contaminants.
4. Floating Tank: After screening, the plastic waste goes into a water-filled floating tank. Plastics with a density less than water (such as PET bottles) will float while heavier materials (like non-plastic contaminants) will sink. This process helps further separate impurities.
5. Conveyor Belt 2: Plastics that have been cleaned in the floating tank move to the second conveyor belt, which leads to the friction washer.
6. Friction Washer: The friction washer is equipped with high-pressure nozzles that spray water onto the plastic waste. Additionally, the friction between the plastic pieces and the interior of the washer helps to remove dirt, labels, and remaining contaminants.
7. Dewatering: The cleaned plastic pieces are then passed through a dewatering stage to remove excess water. This can be done using centrifuges or other dewatering techniques.
8. Shredder: Next, the dried plastic pieces are fed into a shredder. The shredder breaks down the plastic into smaller fragments, making it easier to process and melt down in the recycling phase.
9. Melting and Extrusion: The shredded plastic fragments are melted and formed into pellets through extrusion. These pellets are now ready to be used as raw material for manufacturing new plastic products.
10. New Plastic Product Manufacturing: The recycled plastic pellets can be used to manufacture a wide range of plastic products, such as containers, packaging materials, furniture, and more.
11. Quality Control: Throughout the process, regular quality checks should be conducted to ensure that the recycled plastic meets required standards for strength, purity, and other properties.
12. Distribution: The new plastic products made from recycled materials are distributed for sale and use in the market.
Advantages
An integrated waste management system for plastic recycling offers numerous advantages, both for the environment and society as a whole. Here are some key benefits:
- Resource Conservation: Recycling plastic reduces the need for new plastic production, which conserves valuable natural resources like petroleum, natural gas, and water.
- Energy Savings: Recycling plastic typically requires less energy compared to producing new plastic from raw materials. This leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to overall energy conservation.
- Waste Reduction: By recycling plastic, the amount of plastic waste sent to landfills and incineration facilities is significantly reduced. This helps alleviate the burden on waste management infrastructure and reduces the environmental impact of plastic waste disposal.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: The recycling process generates fewer carbon emissions compared to the production of new plastic. This contributes to mitigating climate change and reducing air pollution.
- Promotion of Circular Economy: Recycling plastic promotes the concept of a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled, minimizing the need for constant extraction of new resources. This approach is more sustainable in the long run.
- Job Creation: The recycling industry creates job opportunities in collection, sorting, processing, and manufacturing. This can contribute to local economies and employment rates.
- Reduced Environmental Pollution: Plastic waste in the environment poses a serious threat to ecosystems and wildlife. By recycling plastic, the likelihood of plastic waste entering oceans, rivers, and other natural habitats is significantly reduced.
- Conservation of Marine Life: Proper plastic recycling helps prevent marine pollution. Marine animals can ingest or become entangled in plastic waste, causing harm to ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Promotion of Innovation: The challenge of recycling plastic has led to innovations in technology and processes, driving advancements in recycling techniques and creating opportunities for research and development.
- Public Awareness and Education: Integrated waste management systems raise public awareness about plastic pollution and the importance of recycling. Education campaigns can encourage responsible consumer behavior and waste disposal practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions are implementing regulations and policies to promote recycling and reduce plastic waste. An integrated waste management system positions businesses to comply with such regulations and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: While the initial investment in recycling infrastructure might be significant, over time, the cost of raw materials and waste disposal can be reduced, leading to long-term cost savings.
- Social Responsibility: Embracing a comprehensive waste management system for plastic recycling demonstrates a commitment to corporate social responsibility, which can enhance a company’s reputation and relationships with customers and stakeholders.
- Global Collaboration: The issue of plastic pollution is global. By adopting effective waste management practices, countries and industries can collaborate on a common cause to mitigate the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Overall, an integrated waste management system for plastic recycling aligns with sustainable development goals, reduces negative environmental impacts, and contributes to a cleaner and healthier planet for current and future generations.
questions asked on integrated waste management for plastic recycling at science exhibition with answers
Question 1: What is integrated waste management for plastic recycling?
Answer: Integrated waste management for plastic recycling is a comprehensive approach that involves collecting, sorting, cleaning, and processing plastic waste to create new products, reducing the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Question 2: How is plastic waste collected and sorted for recycling?
Answer: Plastic waste is collected from various sources, such as households and businesses, and then sorted based on different types of plastics using manual or automated methods.
Question 3: What happens to plastic waste after it is sorted?
Answer: After sorting, plastic waste undergoes cleaning and preprocessing, which involves washing, shredding, and removing contaminants. This prepares the plastic for recycling.
Question 4: What are some common methods of plastic recycling?
Answer: Plastic recycling methods include mechanical recycling (melting and molding), chemical recycling (breaking down plastics into monomers), pyrolysis (heating to break down plastics), and depolymerization (breaking down into monomers).
Question 5: How is recycled plastic used to create new products?
Answer: Recycled plastic is processed and molded into new products, such as packaging materials, furniture, clothing, and toys.
Question 6: What role does public awareness play in plastic recycling?
Answer: Public awareness is crucial for encouraging responsible plastic disposal, promoting recycling habits, and reducing plastic waste generation.
Question 7: How does integrated waste management contribute to a circular economy?
Answer: Integrated waste management aligns with the circular economy by promoting the recycling and reuse of plastic materials, reducing the need for virgin plastic production.
Question 8: What are the environmental benefits of plastic recycling?
Answer: Plastic recycling helps conserve natural resources, reduces energy consumption, minimizes landfill waste, and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
Question 10: What are some challenges in plastic recycling and how can they be addressed?
Answer: Challenges include contamination in plastic waste and lack of awareness. Addressing these challenges requires better waste segregation, improved recycling technologies, and effective public education.

