Introduction:
Ladies and gentlemen, distinguished guests, and fellow advocates of sustainable practices,
Today, I am delighted to present a science project that delves into the transformative world of sustainable agriculture.
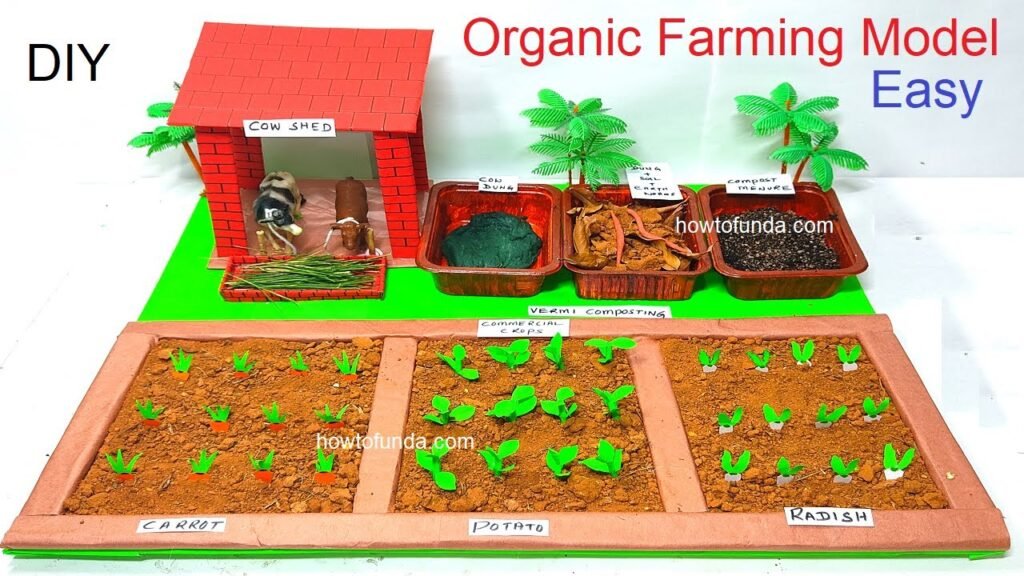
As we gather here at this science exhibition, let us embark on a journey to understand the science behind sustainable farming, its critical role in addressing global food challenges, and its potential to pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
The Challenge of Feeding the World:
Our world faces a daunting challenge – feeding a growing global population while safeguarding the environment. Sustainable agriculture emerges as a powerful solution to this complex problem.
The Science of Sustainable Agriculture:
- Soil Health: Sustainable farming starts with nurturing the soil. Healthy soil is rich in nutrients and microorganisms that support plant growth. Practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage help maintain soil health.
- Water Conservation: Sustainable agriculture minimizes water use through practices like drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and precision farming.
- Biodiversity: Encouraging biodiversity in agricultural landscapes helps control pests, improve pollination, and enhance overall ecosystem health.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming eschews synthetic pesticides and fertilizers in favor of natural alternatives, promoting soil and environmental health.
- Regenerative Agriculture: This approach seeks to restore and revitalize ecosystems by reducing chemical use, enhancing biodiversity, and sequestering carbon in the soil.
The Significance of Sustainable Agriculture:
- Food Security: Sustainable farming practices ensure long-term food security by preserving soil fertility and minimizing environmental degradation.
- Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable agriculture reduces the environmental impact of farming, including soil erosion, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resilience: Sustainable practices make agriculture more resilient to climate change, extreme weather events, and disease outbreaks.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While sustainable agriculture offers numerous benefits, it also faces challenges like resistance to change, initial investment costs, and the need for education and training.
However, these challenges are outweighed by the opportunities for a greener and more sustainable future.
Our Role in Nurturing Sustainable Agriculture:
- Consumer Choices: Support sustainable agriculture by choosing products with eco-friendly certifications and supporting local farmers.
- Advocacy: Advocate for policies that promote sustainable farming practices and provide incentives for environmentally responsible agriculture.
- Education: Educate ourselves and others about the importance of sustainable agriculture and its role in addressing global food challenges.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sustainable agriculture is not just a science project; it is a visionary approach to farming that embodies our commitment to a greener and more sustainable future.
It recognizes the interdependence of food security, environmental health, and agricultural practices.
As we explore the science of sustainable agriculture, let us celebrate its potential to nourish both our bodies and our planet.
Let us embrace the principles of sustainable farming, support local farmers, and work towards a future where environmentally responsible food production is the norm.
Thank you for joining me on this journey to understand the science and significance of sustainable agriculture and the vital role we all play in cultivating a greener future.

