Solar energy is a versatile and renewable resource that offers a wide range of applications across various sectors.
Here’s a depiction of some key uses of solar energy:
- Residential Solar Panels: Solar panels installed on rooftops of homes and buildings capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity can power households, reducing reliance on grid-based electricity.
- Solar Water Heating: Solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water for domestic use, such as bathing and cleaning. These systems can be installed on rooftops or other open areas.
- Solar Street Lights: Solar-powered street lights use photovoltaic panels to charge during the day and provide illumination during the night, enhancing safety in urban and rural areas.
- Solar-Powered Vehicles: Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles can be powered by solar panels integrated into their design. Solar energy assists in charging batteries and extending driving ranges.
- Off-Grid Power Solutions: Solar energy is employed to provide electricity in remote areas without access to traditional power grids. These systems often include batteries for energy storage.
- Solar-Powered Water Pumps: Solar pumps are used for agricultural irrigation and water supply in rural areas, decreasing dependence on fossil fuel-powered pumps.
- Solar-Powered Gadgets: Small solar panels can power portable electronic devices like mobile phones, laptops, and chargers, making them useful for outdoor activities.
- Solar-Powered Desalination: Solar energy is harnessed to power desalination processes, converting seawater into freshwater, which is particularly valuable in water-scarce regions.
- Solar-Powered Ventilation: Solar attic fans use solar panels to power ventilation systems, regulating indoor temperatures and reducing the need for air conditioning.
- Solar Cooking: Solar cookers use sunlight to cook food, reducing the use of traditional cooking fuels and promoting sustainable cooking practices.
- Solar-Powered Refrigeration: Solar-powered refrigerators and coolers are used to store vaccines, medicines, and food in remote or off-grid locations.
- Solar-Powered Charging Stations: Solar charging stations provide a renewable energy source for electric vehicles, encouraging eco-friendly transportation options.
- Solar-Powered Water Treatment: Solar-powered water treatment systems purify water using sunlight, offering clean drinking water solutions in areas with limited infrastructure.
- Solar-Powered Educational Tools: Solar kits and educational models teach students about solar energy, its conversion, and its applications in a hands-on manner.
Depicting these diverse uses of solar energy helps showcase its significance in reducing carbon emissions, increasing energy independence, and contributing to a sustainable future.
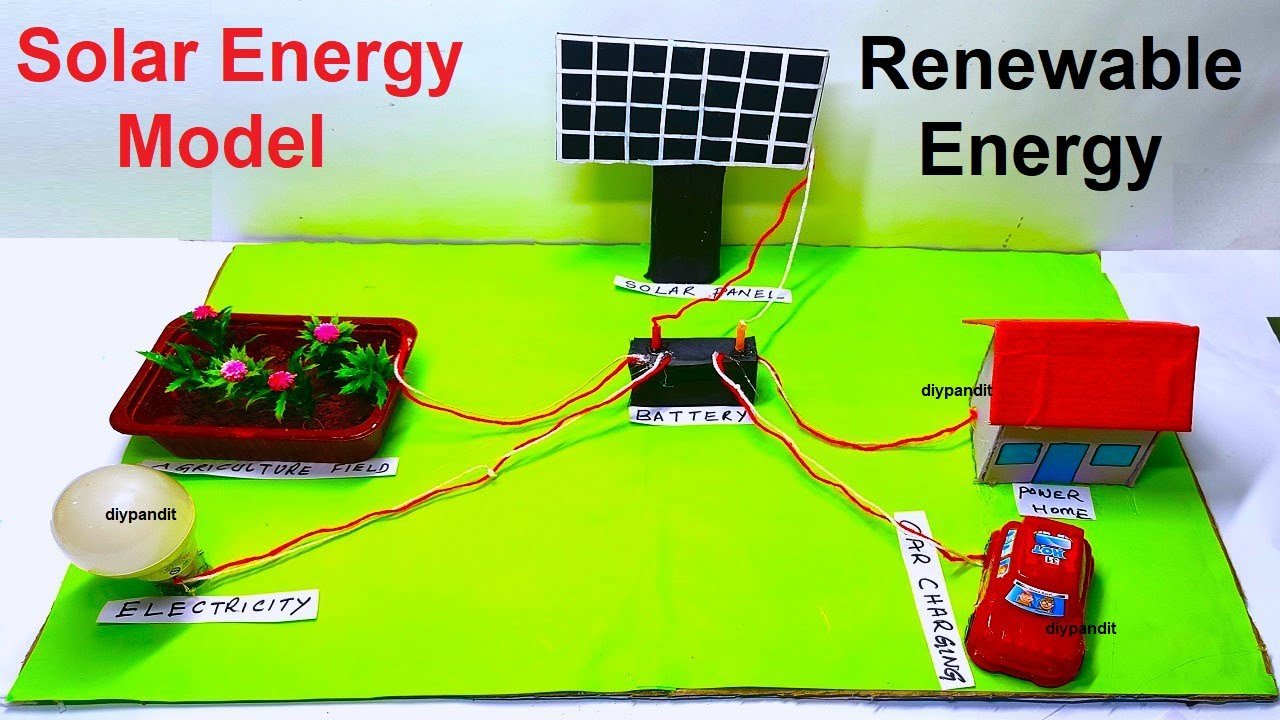
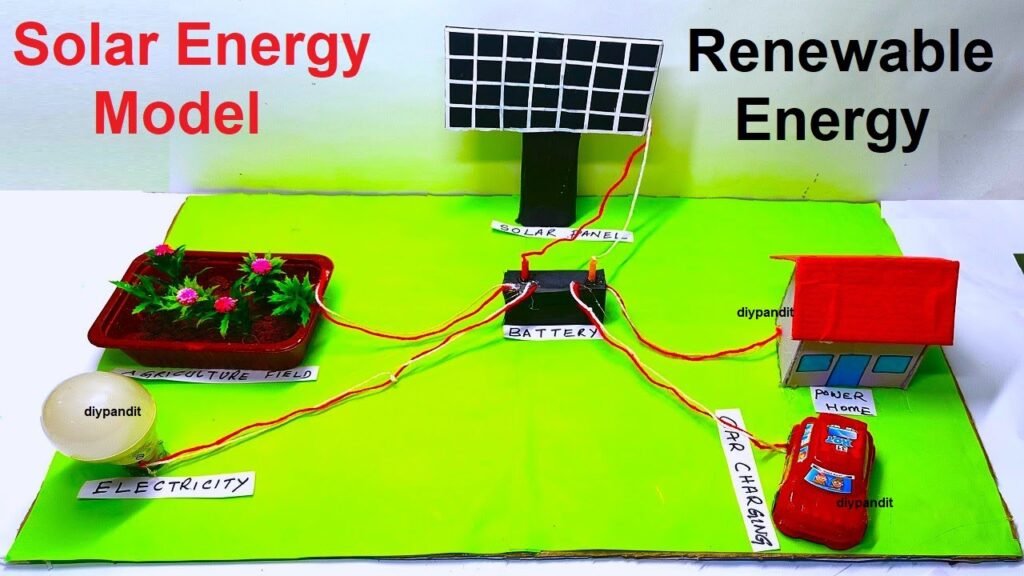
Creating a solar energy uses model using cardboard, colored paper, LED bulbs, a house, a car with a solar charging station, and a plastic tray for solar agriculture is a fantastic way to showcase the diverse applications of renewable solar energy.
Here’s how you can build this model:
Materials You’ll Need:
- Cardboard sheets (for base, structure, and objects)
- Colored paper (for representing objects and details)
- LED bulbs (to represent lights)
- Miniature house model (to represent residential use)
- Toy car (to represent transportation)
- Plastic tray (for solar agriculture)
- Craft knife or scissors
- Hot glue gun and glue sticks
- Craft supplies for decoration (markers, stickers, etc.)
Steps to Build solar energy uses model (renewable solar energy):
- Prepare the Base:
- Cut a large piece of cardboard to use as the base of your model.
- Create the Solar Panel Structure:
- Cut and assemble cardboard pieces to create a solar panel structure.
- Attach the solar panels to the structure using colored paper.
- Position LED Bulbs:
- Attach LED bulbs to the structure to demonstrate indoor lighting powered by solar energy.
- Place the House and Car with Solar Charging Station:
- Position the miniature house and toy car on the base.
- Create a solar charging station near the car using cardboard and colored paper.
- Set Up Solar Agriculture:
- Place the plastic tray with mini plants to represent solar-powered agriculture.
- Decoration:
- Decorate the cardboard structure, base, house, car, and charging station with craft supplies to make it visually appealing.
Model Interaction:
- Place the model in direct sunlight to demonstrate how solar panels collect energy and power the LED bulbs.
- Discuss how solar energy is used for lighting, residential power, transportation (with the solar charging station), and agriculture.
This model effectively showcases a range of practical applications of solar energy, from indoor lighting and residential power to solar-powered transportation and agricultural practices. It’s an engaging and educational way to learn about the versatility of renewable energy sources.
solar energy uses questions asked in science exhibition with answers?
Question 1: How is solar energy harnessed for electricity generation?
Answer: Solar energy is captured using photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar panels. These panels contain semiconductor materials that convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Question 2: Can solar energy be used at night or on cloudy days?
Answer: Solar panels primarily generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. However, energy storage solutions like batteries can store excess solar energy during sunny days for use at night or on cloudy days.
Question 3: What are some common residential uses of solar energy?
Answer: Solar energy is used for residential purposes in various ways, including rooftop solar panels for electricity, solar water heaters, and solar-powered outdoor lighting.
Question 4: How does solar energy contribute to reducing carbon emissions?
Answer: Solar energy is a clean and renewable source, producing no greenhouse gas emissions during its operation. Using solar energy helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigates climate change.
Question 5: Are solar-powered vehicles practical for everyday use?
Answer: Solar panels can contribute to charging electric vehicle (EV) batteries, extending their range. While fully solar-powered cars are less common, hybrid and plug-in hybrid EVs can benefit from solar-assisted charging.
Question 6: What is the significance of solar-powered water pumps?
Answer: Solar-powered water pumps provide sustainable irrigation and water supply solutions in remote areas. They reduce the dependence on fossil fuels for water pumping.
Question 7: How do solar-powered gadgets work?
Answer: Small solar panels integrated into gadgets capture sunlight, convert it into electricity, and charge internal batteries, allowing these devices to function without the need for traditional power sources.
Question 8: Can solar energy be used for large-scale power generation?
Answer: Yes, solar farms consist of multiple solar panels connected to the grid, generating significant amounts of electricity. These installations contribute to the overall power supply.
Question 9: What is solar desalination and why is it important?
Answer: Solar desalination uses solar energy to remove salt and impurities from seawater, providing freshwater in regions with limited access to clean water sources.
Question 10: How can solar energy address energy poverty?
Answer: Solar energy can provide electricity to areas without access to traditional power grids. Off-grid solar systems, such as solar lanterns and microgrids, offer energy solutions in remote locations.
Question 11: How can solar energy be used for educational purposes?
Answer: Solar energy educational kits and models teach students about renewable energy, energy conversion, and sustainability in an interactive and engaging way.
Question 12: Are there initiatives to promote solar energy adoption?
Answer: Many governments offer incentives, subsidies, and policy support to encourage the adoption of solar energy, making it more accessible and affordable for individuals and businesses.