Introduction:
In this topic, we show a model of heart for school science exhibition. We use very simple materials that are easily available.
The human heart is the organ in the body that pumps
It provides the body with necessary nutrients for its proper functioning. The human heart is located between the lungs.
The human heart is typically the size of one’s own fist. The pericardium is a double-walled sac that protects the heart and anchors it to the chest.
The heart wall consists of 3 layers, epicardium, myocardium and endocardium. I am explaining each layer as below
Epicardium layer lubricates the heart and protects it from outside.
The myocardium is the muscular layer that is responsible for pumping blood into the heart.
Endocardium layer is the squamous endothelium layer that allows the blood to stick to the heart.
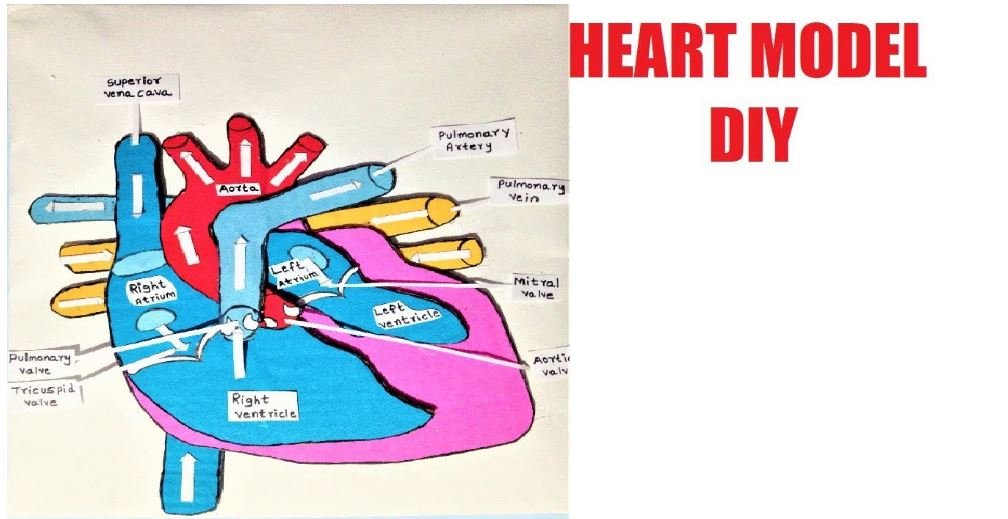
There are four chambers of the heart, 2 atriums,
A system of valves is present in the heart that is responsible for helping the blood flow happen in the right direction.
Materials Used to Make Heart Model
- Cardboard
- Pencil
- Scissors
- Paints and brushes
- Red, blue, light blue, pink and yellow Colour paper
- Liquid glue
- Hot glue gun
- Chart Sheet – White
You use the resource/tools page section to find the tips where you can buy these materials used at a reasonable cost.
Detailed Video Show How To Make Heart Model Making for School Science Project
Prepare for Science Fair Questions & Answers – Heart Model
- What are the functions of the heart?
A. The main function of the heart is to take the deoxygenated blood through the veins to the lungs for oxygenation before it is passed to the blood vessels to other parts of the body through the arteries.
2. Can you name four chambers of the heart?
A. There are four chambers of the heart, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle.
The atria are smaller than the ventricles and are responsible for carrying the blood to the lungs.
Ventricles are larger than the atria and are stronger than them so that they can pump blood back into the blood vessels to various organs of the body.
3. Explain the physiology of heart?
A. At any given point of time, the heart is in one of the states: diastole and systole.
During the diastole, the cardiac muscle tissue is in the state of contraction, so that the blood is pushed out of the chamber and during systole, the cardiac muscle tissue is in the state of relaxation wherein the chamber is filled with blood.
4. Explain the blood flow through the heart?
A. Deoxygenated blood that returns from the body to the heart enters the heart through the chambers called as atria through the veins.
Then, it is pumped into the left ventricle into the pulmonary trunk for oxygenation. In the pulmonary trunk, the lungs release carbon dioxide and absorb oxygen.
Through the pulmonary veins, the blood is pumped back to the heart in the left atrium. From here, the blood enters into the aorta through the right ventricle and thus to the organs of the body.
Conclusion:
It is very important that the proper functioning of the heart is maintained as it affects the life of the person.
These days, heart problems have become very common which is attributed to various factors. Diseases related to heart are called cardiovascular diseases.
A healthy and normally functioning heart shows systole and diastole range of 120/80. Anything above or below it is considered as to suffering from blood pressure.

