Introduction:
Computer networks are intricate systems that facilitate the exchange of data and resources among various devices.
They form the backbone of modern communication and information sharing, enabling people and organizations to connect and collaborate across different locations.
There are several types of computer networks, each designed to suit specific needs and scales of operation.
- Local Area Network (LAN): A LAN is a network confined to a relatively small geographic area, like a home, office, or a campus. It connects devices such as computers, printers, and servers, allowing them to share resources like files, applications, and internet access. LANs are characterized by high data transfer rates and low latency.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): WANs cover larger geographical areas, often spanning cities, countries, or even continents. These networks connect multiple LANs and are typically managed by service providers. WANs utilize various technologies like leased lines, satellites, and fiber-optic cables to ensure data transmission across long distances.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN lies between a LAN and a WAN in terms of size, covering a larger area than a single LAN but smaller than a WAN. MANs are often used to connect multiple buildings within a city or town, such as different branches of a corporation or university campuses.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): A PAN is the smallest and most personal type of network. It connects devices within the immediate vicinity of an individual, typically within a range of a few meters. Bluetooth technology is a common example of PAN, used for connecting devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearable gadgets.
- Home Area Network (HAN): A HAN is specific to a residential setting, connecting devices within a single household. It allows for the integration and sharing of various technologies like computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and appliances.
- Campus Area Network (CAN): A CAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN, covering a campus or a large institution like a university. It connects multiple buildings within a limited geographic area, providing high-speed connectivity for academic, administrative, and research purposes.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN is a secure network that leverages public infrastructure, like the internet, to connect remote users or sites. It creates a private network over a public one, ensuring secure data transmission through encryption protocols.
- Intranet and Extranet: These are private networks used by organizations for internal communication and collaboration. An intranet is confined to an organization’s internal users, while an extranet extends the network to include external partners, suppliers, or clients.
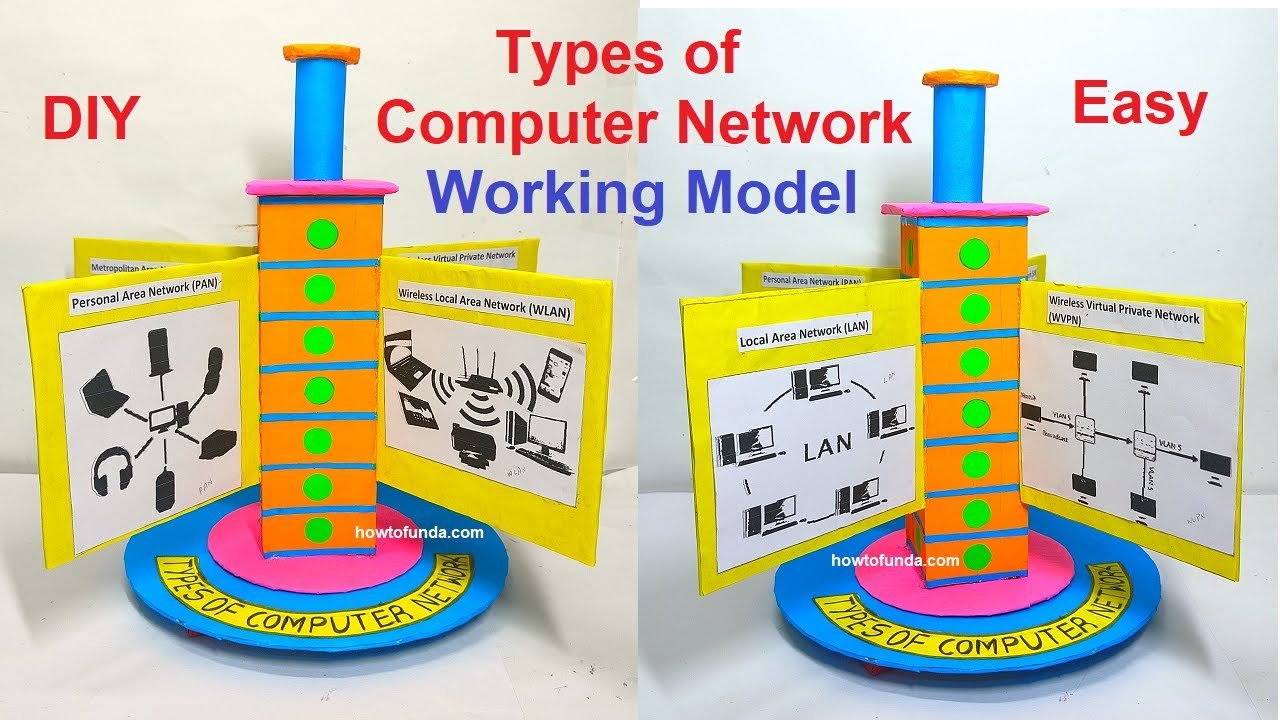
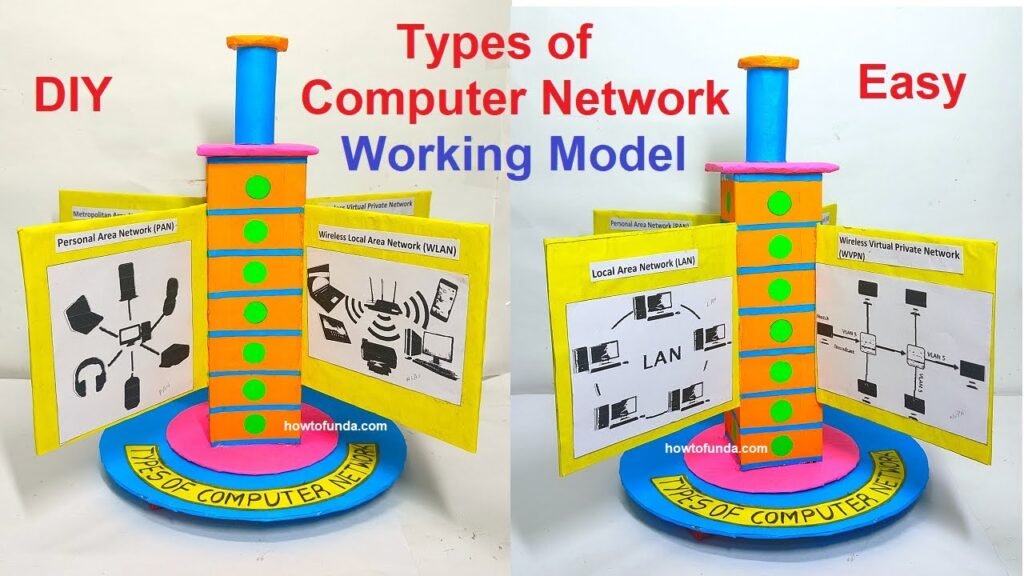
Construction of the 3d Working Model
In this project, we will construct a 3D working model that showcases different types of computer networks using cardboard and colored paper.
The model will be partitioned to represent distinct network types (e.g., LAN, WAN, MAN).
Additionally, the model will be manually rotatable to allow for interactive exploration.
This hands-on project serves as an engaging educational tool to visually understand various network types. Let’s proceed with building this comprehensive computer network model!
Materials Needed:
- Cardboard sheets
- Colored paper or construction paper
- Scissors
- Glue or adhesive tape
- Markers or pens
- Pencil
- Craft knife (optional, for precise cutting)
- Small rotating platform (e.g., Lazy Susan base, optional but recommended)
Building the Network Model:
1. Base Structure:
Step 1: Create the Base
- Cut out a large circular piece of cardboard to serve as the base of the model. This circular base will allow for easy rotation.
Step 2: Reinforce the Base
- Attach additional layers of cardboard underneath the base to provide stability, especially if a rotating platform is not used.
2. Partitioning for Network Types:
Step 3: Designing Network Partitions
- Cut out smaller circles from colored paper to represent different network types (e.g., LAN, WAN, MAN). Label each partition accordingly.
Step 4: Attaching Partitions
- Glue or tape each partition onto the base, evenly spaced around the circle. These partitions will act as the segments representing different network types.
3. Creating Network Elements:
Step 5: LAN (Local Area Network)
- Within the LAN segment, create miniatures of computers, printers, and other devices using colored paper. Attach these devices to represent a LAN.
Step 6: WAN (Wide Area Network)
- In the WAN segment, craft miniature representations of remote locations or cities, labeling them to indicate different geographical areas connected by the WAN.
Step 7: MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Within the MAN segment, create medium-sized structures (e.g., buildings) representing different locations within a city or metropolitan area.
4. Manual Rotation Mechanism:
Step 8: Preparing the Rotating Platform
- If using a rotating platform, attach it securely to the bottom of the cardboard base. Ensure it allows for smooth manual rotation.
Step 9: Final Assembly
- Double-check that all components are securely attached, and the model is balanced. Ensure that it rotates smoothly.
Conclusion:
Through this hands-on project, we’ve successfully constructed a 3D working model showcasing different types of computer networks.
This interactive model provides a visual representation of LANs, WANs, and MANs, enhancing understanding of network concepts.
The manual rotation feature allows for interactive exploration, making it an engaging educational tool.