1. Introduction
The human heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It supplies oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removes carbon dioxide and waste products.

The heart works as a pump in the circulatory system, functioning non-stop from birth to death. On average, the heart beats 72 times per minute and pumps around 5 liters of blood per minute.
2. Location and Size of Human Heart
- The heart is located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, slightly tilted to the left.
- It is about the size of a fist (≈ 12 cm long, 8 cm wide).
- Average weight: 250–300 g in females, 300–350 g in males.
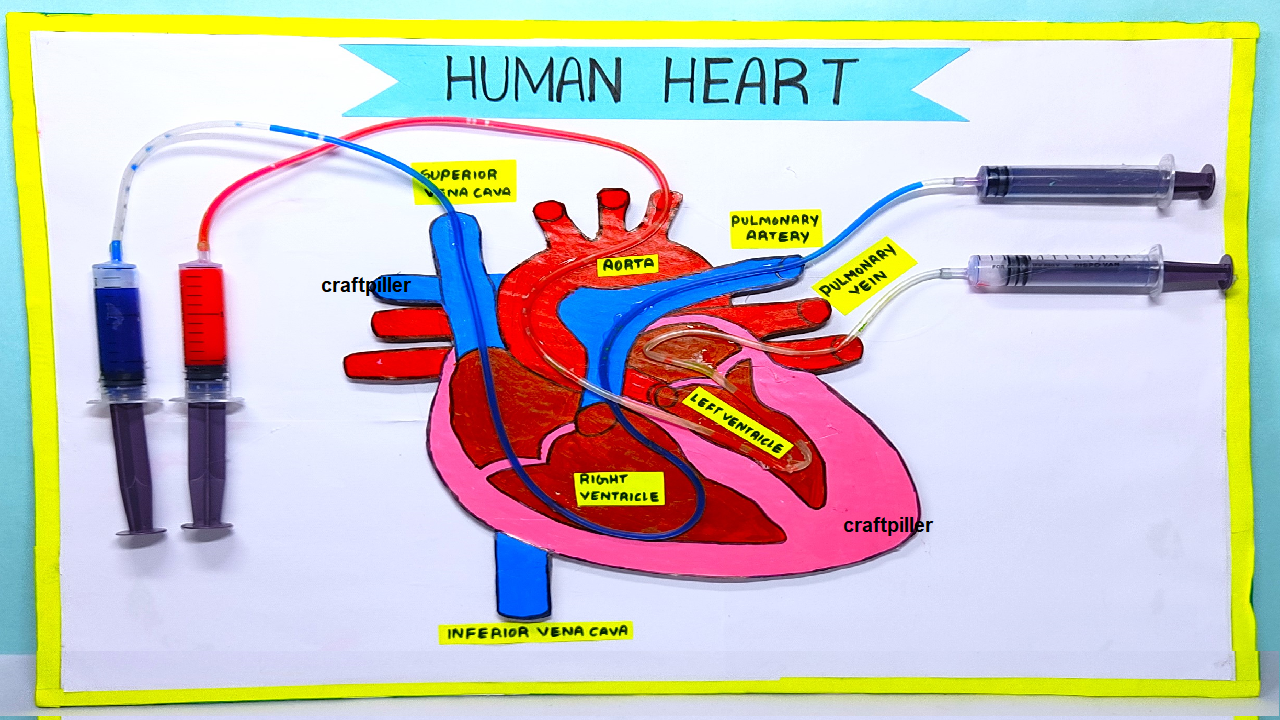
3. Structure of Heart
The heart is a hollow, muscular organ made of cardiac muscles. It is enclosed in a protective sac called pericardium, which contains pericardial fluid to reduce friction.
The walls of the heart have three layers:
- Epicardium (outer layer)
- Myocardium (thick muscular middle layer)
- Endocardium (inner smooth layer)
4. Chambers of the Heart

The heart is divided into four chambers:
- Right Atrium – receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
- Right Ventricle – pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs.
- Left Atrium – receives oxygenated blood from lungs.
- Left Ventricle – pumps oxygenated blood to entire body.
The left ventricle has the thickest muscular wall because it must pump blood at high pressure to all parts of the body.
5. Valves of the Heart
Valves prevent backflow of blood and ensure one-way circulation:
- Tricuspid Valve – between right atrium and right ventricle.
- Bicuspid/Mitral Valve – between left atrium and left ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve – between right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Aortic Valve – between left ventricle and aorta.
6. Blood Vessels Connected to the Heart

- Veins (bring blood to heart):
- Superior and Inferior Vena Cava → Right Atrium
- Pulmonary Veins → Left Atrium
- Arteries (carry blood away):
- Pulmonary Artery → Lungs
- Aorta → Whole Body
7. Double Circulation

Human beings have a double circulation system consisting of two pathways:
- Pulmonary Circulation: Right side → Lungs → Left side (blood oxygenated).
- Systemic Circulation: Left side → Body → Right side (blood deoxygenated).
This ensures separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, increasing efficiency.
8. Working of Human Heart (Cardiac Cycle)
The sequence of events in one heartbeat is called cardiac cycle (~0.8 sec).
- Atrial Systole: Atria contract → blood into ventricles.
- Ventricular Systole: Ventricles contract → blood pumped to lungs & body.
- Diastole: Relaxation phase; chambers refill with blood.
Average heartbeat: 72 per minute → ~100,000 times per day.
9. Pulse and Heartbeat
- Pulse: Rhythmic expansion of artery due to ventricular contraction. Normal pulse: 72/min.
- Heartbeat: Sound produced due to closure of valves (“lub-dub” sound).
10. Functions of Heart
- Pumps blood continuously.
- Supplies oxygen and nutrients.
- Removes carbon dioxide and waste.
- Maintains blood pressure.
- Helps regulate body temperature.
- Distributes hormones and immune cells.
11. Control of Heartbeat
The heartbeat is myogenic (originates within the heart itself).
- Controlled by Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) – natural pacemaker.
- SA Node generates electrical impulses → regulate contraction rhythm.
- Artificial pacemakers are used when SA Node fails.
12. Common Diseases of the Heart
- Hypertension (High BP): Strains heart and arteries.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Blockage of arteries due to cholesterol (atherosclerosis).
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): Blood supply to heart muscle blocked.
- Arrhythmia: Irregular heartbeat.
- Congestive Heart Failure: Weak pumping efficiency.
- Rheumatic Heart Disease: Caused by bacterial infection.
13. Preventive Measures for Heart Health
- Avoid junk food; eat a balanced diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Reduce stress.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Maintain healthy body weight.
- Go for regular medical check-ups.
14. Role of Nutrition and Exercise
- Vitamin-rich diet, especially Vitamin B complex, C, E, and Omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fruits like papaya, apple, and citrus.
- Regular aerobic exercise (walking, jogging, swimming) strengthens cardiac muscles.
15. Heart Transplant and Modern Treatments
- Heart Transplant: Replacement of diseased heart with donor heart.
- Bypass Surgery: Creates new route for blood around blocked arteries.
- Angioplasty: Balloon inserted to widen narrowed arteries.
- Stent Implantation: Wire mesh tube placed in artery to keep it open.
- Artificial Hearts: Mechanical pumps used in severe cases.
16. Interesting Facts about Human Heart
- Beats ~2.5 billion times in a lifetime.
- Pumps ~7,000 liters of blood daily.
- Electrical activity of heart continues outside body (used in ECG).
- Left lung is smaller than right to accommodate heart.
- The sound “lub-dub” is due to valve closure.
17. Importance of Heart in Life
The heart is essential for sustaining life by transporting oxygen, nutrients, and hormones. It maintains homeostasis and ensures proper functioning of every cell. Without a healthy heart, survival is impossible.
18. Conclusion
The human heart is a miracle of biology and nature’s pump that works tirelessly from birth to death. This project helped me understand its structure, functioning, and importance in human life.
While modern medicine has advanced to treat heart diseases, prevention through healthy lifestyle, proper diet, and exercise remains the best strategy. A healthy heart means a healthy life.
19. Bibliography
- NCERT Science & Biology Textbooks (Class 9–12)
- Human Physiology by Guyton and Hall
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology by Tortora & Derrickson
- WHO Reports on Cardiovascular Diseases
- Websites: American Heart Association, Khan Academy Biology