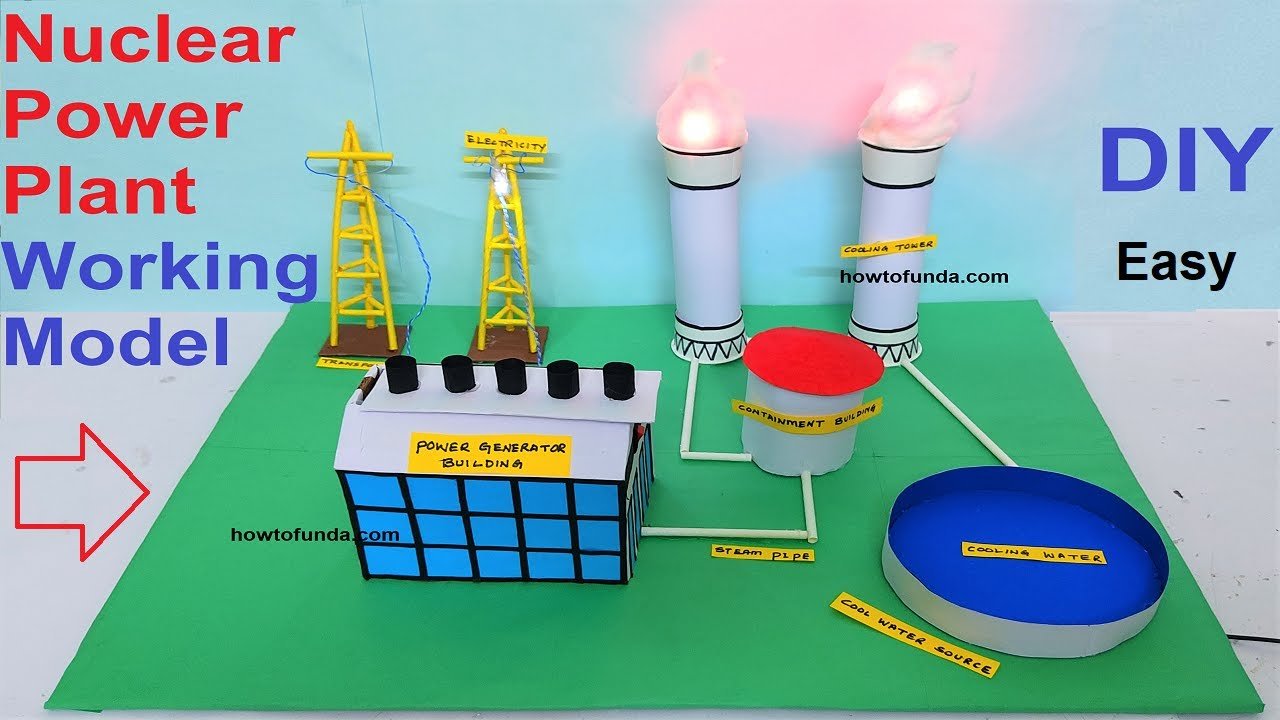
Overview:
Nuclear power plants generate electricity using the heat produced from nuclear fission, a process where the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts.
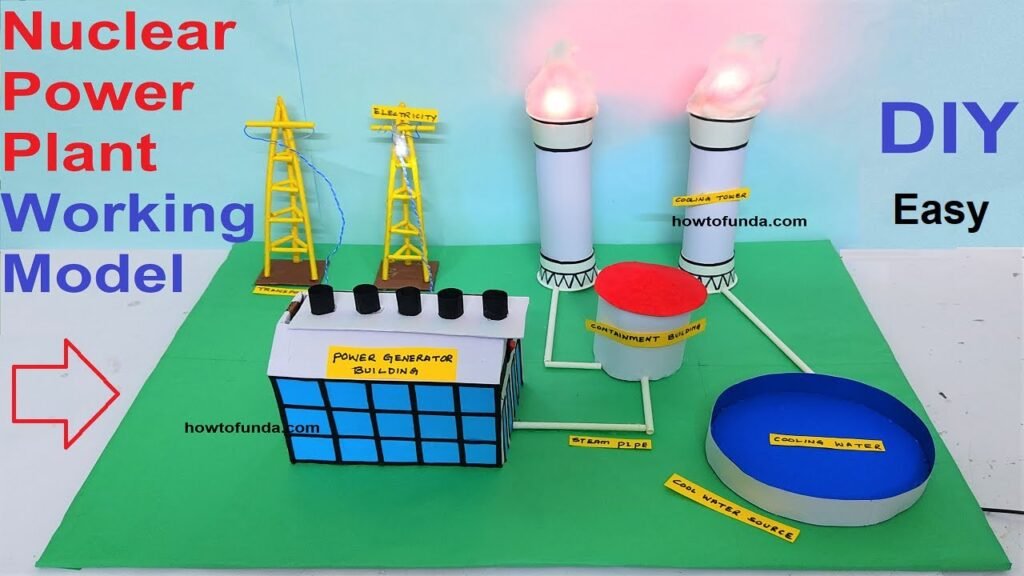
This process releases a significant amount of energy, which is then used to produce steam that drives turbines connected to electricity generators.
Components of the Nuclear power working Model:
Let’s first look at the components of our nuclear power model:
- Reactor Core: Represents the heart of the nuclear power plant where fission occurs.
- Control Rods: These rods control the fission process.
- Cooling System: Keeps the reactor at a safe temperature.
- Steam Generator: Uses the heat from the reactor to convert water into steam.
- Turbine: Driven by steam to produce electricity.
- Generator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Condenser: Cools the steam back into water to be reused.
Demonstration of nuclear power working model :
- Reactor Core and Fission Process:
- The reactor core contains fuel rods made of uranium or plutonium. When these atoms split, they release a lot of energy in the form of heat.
- Use small balls or beads to represent the splitting of atoms. Demonstrate the chain reaction by showing one ball hitting others and causing them to split apart.
- Control Rods:
- Control rods are inserted or withdrawn from the reactor core to control the rate of the nuclear reaction.
- Demonstrate how inserting control rods slows down the reaction and removing them speeds it up using a simple mechanical representation.
- Heat Generation and Steam Production:
- The heat from the fission process is used to heat water in the steam generator, turning it into steam.
- Pour water into a small container and heat it using a safe heat source to create steam. Use a toy steam engine if available to visualize the process.
- Turbine and Generator:
- The steam drives the turbine, which is connected to the generator. As the turbine spins, the generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Use a small fan or windmill to represent the turbine and connect it to a simple generator or motor. Show how the movement of the turbine produces electricity to light up a small bulb.
- Condenser:
- After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled in the condenser and turned back into water, which is then reused in the steam generator.
- Demonstrate the cooling process by passing steam through a coiled tube submerged in cold water and collecting the condensed water at the end.
Real-World Impact Due to Nuclear Power :
- Clean Energy: Nuclear power produces a large amount of electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
- Efficiency: It is one of the most efficient energy sources, providing a steady supply of power.
- Challenges: However, it also presents challenges, such as managing radioactive waste and ensuring the safety of reactors.
Conclusion:
To summarize, our model demonstrates the key components and processes involved in generating electricity from nuclear power. This method provides a substantial amount of clean energy but comes with its own set of challenges.