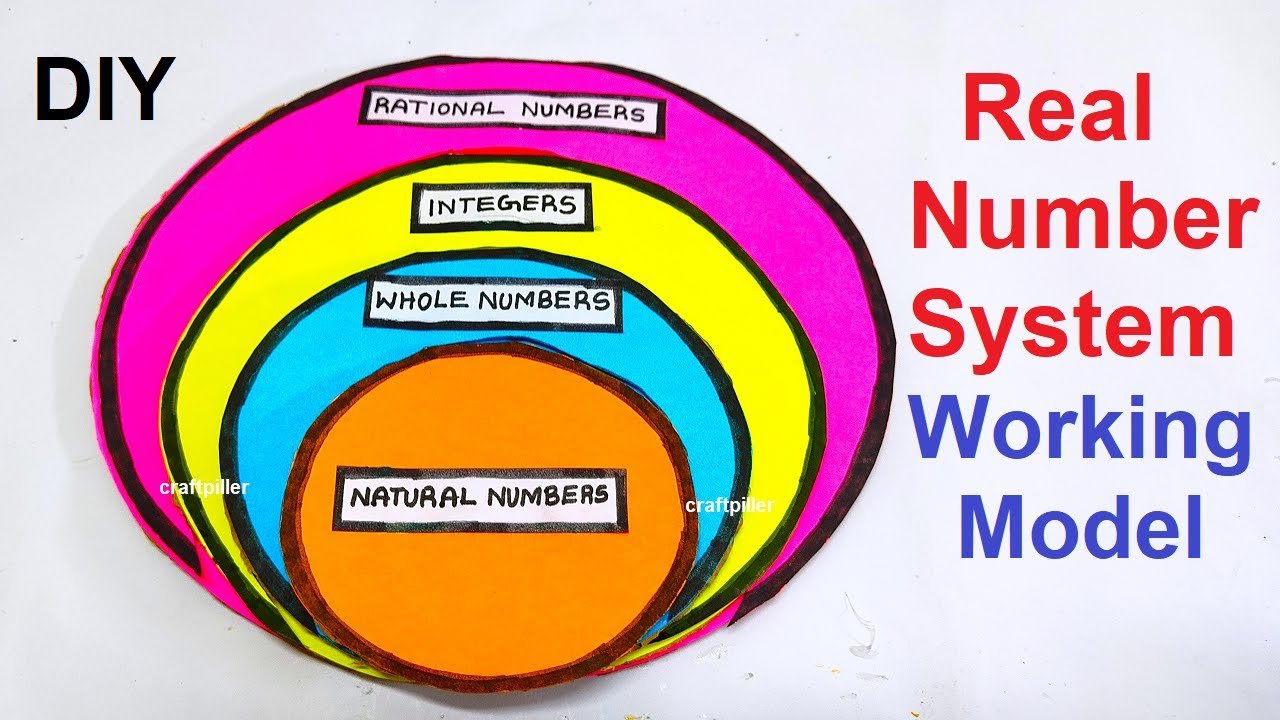
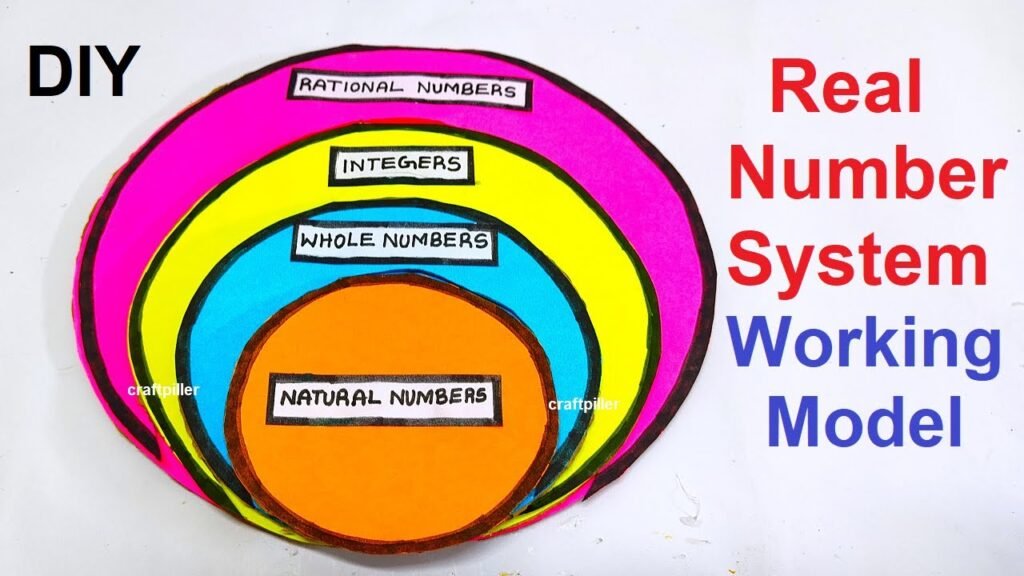
Creating a tangible learning model (TLM) for the real number system using cardboard and color paper can be a fun and effective way to understand this mathematical concept.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to making the TLM:
Materials Needed:
- Cardboard sheet
- Color papers (representing different categories of numbers)
- Scissors
- Glue
- Marker
- Ruler
Procedure:
Step 1: Prepare the Base
- Take a piece of cardboard and cut it into a rectangular base. This will serve as the foundation for your TLM.
Step 2: Define Categories of Numbers
- Use different color papers to represent various categories of numbers:
- Orange paper: Representing natural numbers
- Blue paper: Representing whole numbers
- Yellow paper: Representing integers
- Pink paper: Representing rational numbers
Step 3: Create Number Tiles
- Cut the colored papers into square tiles, making sure each color represents its respective category of numbers. Write down examples of numbers from each category on the corresponding colored tiles.
- For example:
- Orange Tiles (Natural Numbers):
- Tile 1: “1”
- Tile 2: “2”
- Tile 3: “3”
- …
- Blue Tiles (Whole Numbers):
- Tile 1: “0”
- Tile 2: “1”
- Tile 3: “2”
- …
- Yellow Tiles (Integers):
- Tile 1: “-3”
- Tile 2: “-2”
- Tile 3: “-1”
- …
- Pink Tiles (Rational Numbers):
- Tile 1: “1/2”
- Tile 2: “0.75”
- Tile 3: “-3/4”
- ..
- Orange Tiles (Natural Numbers):
- For example:
Step 4: Arrange Tiles
- Place the tiles on the cardboard base in an organized manner, forming a visual representation of the real number system.
Definition and Examples:
- Real Numbers (R): The set of all rational and irrational numbers. This includes numbers like fractions, decimals, square roots, and more.
- Examples: √2, -3/4, 0.5, π, -√3, etc.
- Rational Numbers (Q): Numbers that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers.
- Examples: 1/2, -3/5, 0.75, 2, -7, etc.
- Irrational Numbers (I): Numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. They have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions.
- Examples: √2, π, e, etc.
- Integers (Z): The set of positive whole numbers, negative whole numbers, and zero.
- Examples: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.
- Whole Numbers (W): The set of positive whole numbers and zero.
- Examples: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.
- Natural Numbers (N): The set of positive counting numbers.
- Examples: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, etc.
By creating this real number systems math’s working model or TLM,
students can visually see the relationships between different categories of numbers and gain a better understanding of the real number system.