How the human lungs works?
The lungs are a pair of organs located in the thorax (chest) that are responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment.
The main function of the lungs is to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. This process is known as respiration.
The lungs have a spongy texture and are divided into smaller units called alveoli, where the exchange of gases takes place.
The alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood vessels called capillaries, through which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
When we breathe in, the diaphragm, a muscle located at the base of the lungs, contracts and moves downward.
This causes the chest cavity to expand and create a negative pressure inside the lungs. As a result, air is sucked into the lungs through the nose and mouth, and travels down the trachea (windpipe) and into the lungs.
Oxygen from the air diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the bloodstream, where it binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells and is transported to the body’s cells.
When we breathe out, the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward. This causes the chest cavity to decrease in size and the air inside the lungs to be pushed out.
The carbon dioxide from the body’s cells diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the bloodstream, where it is carried to the lungs and exhaled out of the body.
The lungs also have a protective mechanism to remove foreign particles such as dust and bacteria, by means of cilia, tiny hair-like structures in the airways that move in coordinated waves to help move mucus and trapped particles out of the lungs.
Overall, the lungs play a vital role in maintaining the body’s oxygen and carbon dioxide levels and are essential for life.
Step by step of making of the lungs working model
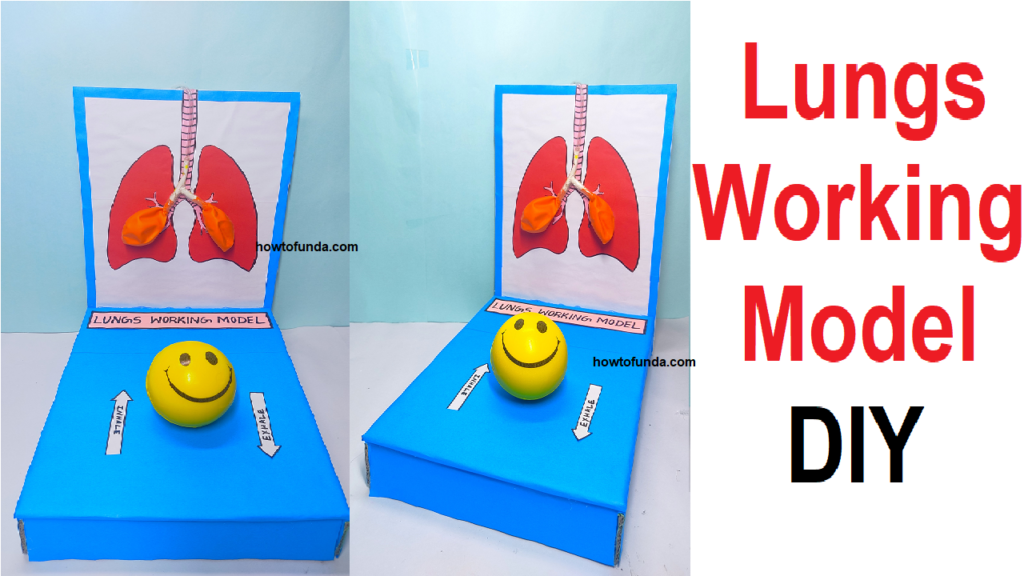
A lungs working model science project using a balloon and a spongy ball can demonstrate the basic functions of the lungs and the respiratory system.
Here are the steps to make a simple lungs working model using a balloon and a spongy ball:
- You will need a balloon, a spongy ball, a straw or pipe, and a cardboard
- As you press on the spongy ball ,the balloon will inflate and deflate, simulating the movement of the lungs during breathing. The spongy ball represents the diaphragm and the balloon represents the lungs.
- You can add labels to the model to show the different parts and explain how it works.
Step by Step video instructions on making lungs working model
What are the lungs and where are they located in the body?
The lungs are a pair of organs located in the thorax (chest) that are responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment.
What is the main function of the lungs?
The main function of the lungs is to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, through a process called respiration.
How are the lungs structured?
The lungs have a spongy texture and are divided into smaller units called alveoli, where the exchange of gases takes place.
The alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood vessels called capillaries, through which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
What is the role of the diaphragm in the respiratory process?
The diaphragm is a muscle located at the base of the lungs that contracts and relaxes during breathing. When it contracts,
it causes the chest cavity to expand and create a negative pressure inside the lungs, allowing air to enter.
When it relaxes, it causes the chest cavity to decrease in size and air to be pushed out of the lungs.
How does the body remove foreign particles from the lungs?
The body has a protective mechanism to remove foreign particles such as dust and bacteria, by means of cilia, tiny hair-like structures in the airways that move in coordinated waves to help move mucus and trapped particles out of the lungs.
How does oxygen and carbon dioxide get in and out of the body through the lungs?
When we breathe in, oxygen from the air diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the bloodstream, where it binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells and is transported to the body’s cells.
When we breathe out, carbon dioxide from the body’s cells diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the bloodstream, where it is carried to the lungs and exhaled out of the body.

