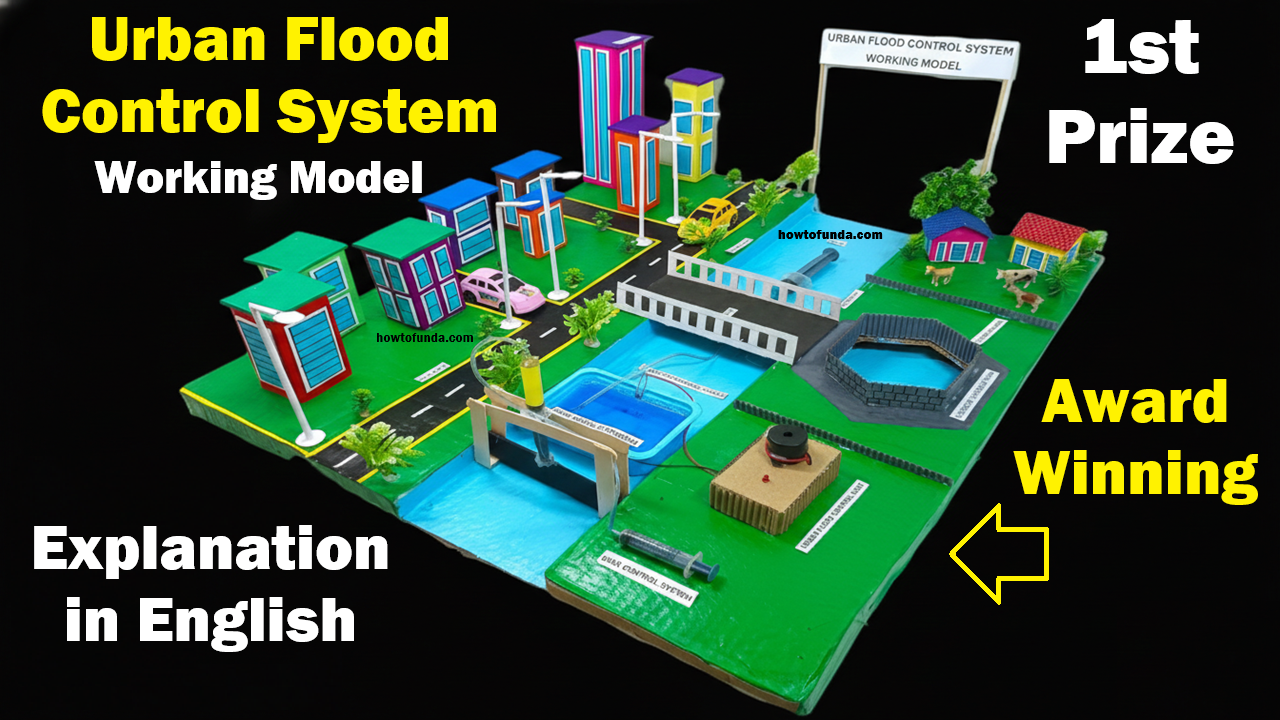
Urban flooding is one of the biggest environmental challenges faced by modern cities.
Rapid urbanization, concrete roads, poor drainage systems, and climate change have increased the risk of floods in urban areas.
To understand and demonstrate flood management techniques, an Urban Flood Control Working Model is an excellent science exhibition project.
This award-winning DIY project clearly explains how cities can manage excess rainwater using smart drainage and water storage systems.
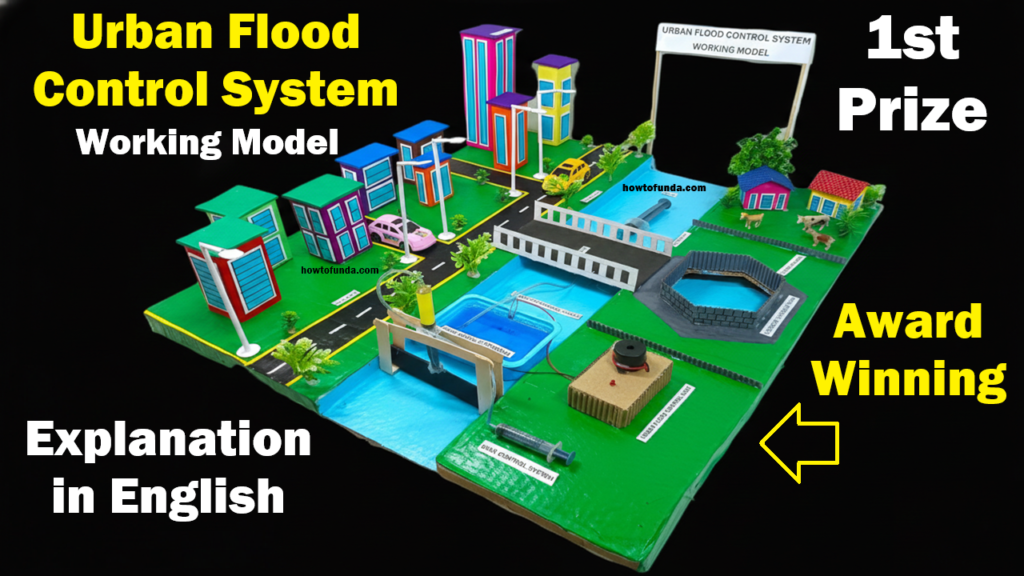
Introduction to Urban Flooding
Urban flooding occurs when heavy rainfall exceeds the capacity of drainage systems in cities. Unlike rural areas, cities have more concrete surfaces like roads, buildings, and pavements. These surfaces do not allow rainwater to seep into the ground. As a result, water accumulates on roads and low-lying areas, causing traffic jams, property damage, and health hazards.
This working model demonstrates how floodwater can be controlled using drainage channels, storage tanks, water pumps, and filtration systems.
Objective of the Model
The main objectives of this project are:
- To demonstrate how urban flooding occurs.
- To show how proper drainage systems can reduce water accumulation.
- To explain rainwater harvesting and reuse.
- To promote sustainable city planning.
- To create awareness about flood management techniques.
Materials Required
Here is the list of materials needed to make the model:
- Thermocol or wooden base board
- Cardboard sheets for buildings
- Colored papers and paints
- Plastic pipes (for drainage system)
- Transparent plastic containers (for water tanks)
- Small water pump (optional for working model)
- DC motor and battery
- LED lights (optional)
- Glue gun and adhesive
- Artificial grass sheets
- Toy cars and trees (for decoration)
- Cutter and ruler
- Water and blue food color
Layout Design of the Model
The model consists of:
- Residential and commercial buildings
- Roads with drainage lines
- Main drainage canal
- Underground water storage tank
- Rainwater harvesting pit
- Flood barrier system
- Water pumping system
The layout should represent a small city area divided into sections such as residential area, commercial area, and water management area.
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Prepare the Base
Take a large thermocol, cardboard or wooden base and cover it with green sheet or paint to represent land. Divide the base into sections using pencil markings.
Step 2: Construct Buildings
Make small buildings using cardboard. Paint them with bright colors to make the model attractive. Fix them on one side of the base to represent an urban area.
Step 3: Design Roads and Drainage
Create black roads using chart paper. On both sides of the roads, place small drainage pipes. Connect all small pipes to a main drainage canal.
This shows how rainwater flows from streets to larger drains.
Step 4: Create Rainwater Collection Area
Attach plastic pipes to connect drains to a transparent water storage tank. This tank represents underground water storage.
You can color water blue to show collected rainwater.
Step 5: Install Water Pump (Optional Working Feature)
Attach a small water pump inside the storage tank. Connect it to a higher outlet pipe to demonstrate water pumping to safe areas or reuse systems.
Switch on the motor to show water movement.
Step 6: Add Flood Barrier
Create a small dam-like structure using cardboard near the canal. This represents flood barriers that prevent water from entering residential areas.
Step 7: Demonstrate Flooding
Pour water slowly on the road area to simulate heavy rainfall. Without drainage, water accumulates. When drainage and storage are activated, water flows into the tank.
This clearly shows the importance of flood control systems.
Conclusion
Urban flooding is a serious problem caused by rapid urbanization and climate change. However, proper drainage systems, rainwater harvesting, and smart flood control techniques can reduce the impact significantly.
This Urban Flood Control Working Model helps students understand how scientific planning and engineering solutions can protect cities from flood disasters. It also encourages sustainable development and environmental awareness.