Here’s how to create a Trigonometric Ratios Table Working Model using cardboard, color paper, and a rotating mechanism. This model will visually display the trigonometric ratios in an interactive way.
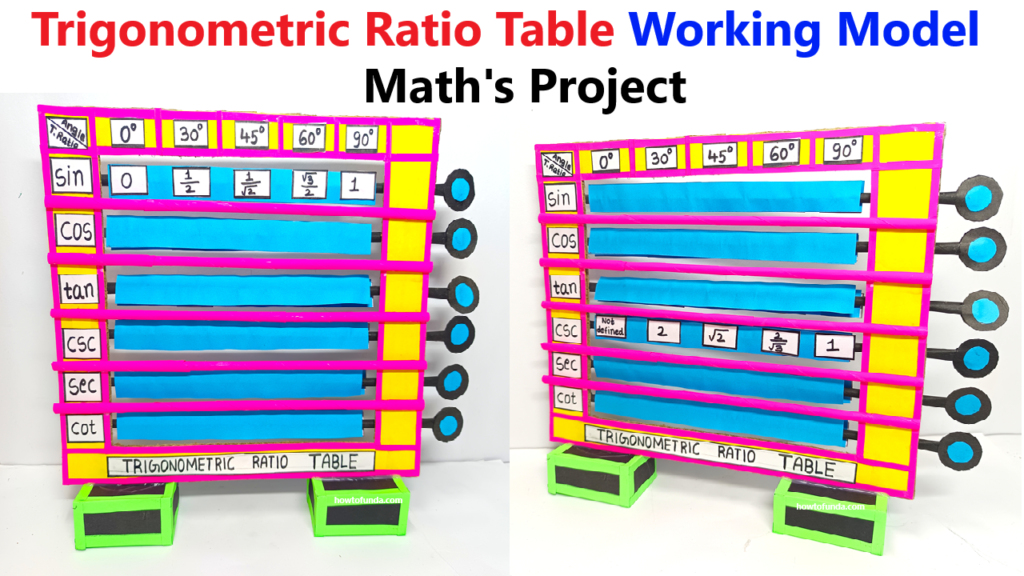
Concept:
The model demonstrates the trigonometric ratios (sinθ\sin \thetasinθ, cosθ\cos \thetacosθ, tanθ\tan \thetatanθ, cscθ\csc \thetacscθ, secθ\sec \thetasecθ, cotθ\cot \thetacotθ) for standard angles (0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°) in a rotating disk format. Users can rotate the disk to align the angle with its corresponding values.
Materials Needed:
- Cardboard: For the base and rotating disks.
- Colored Paper: To decorate and label the model.
- Push Pin: For the rotating mechanism.
- Glue or Tape: To assemble the model.
- Marker/Pens: For writing the ratios and values.
- Ruler and Compass: For precision in drawing circles.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
1. Create the Base:
- Cut a square or circular base out of cardboard (around 12 x 12 inches or 12 inches in diameter).
- Cover it with colored paper for decoration.
- Label the base with the title: “Trigonometric Ratios Table”.
2. Prepare the Rotating Disks:
- Cut two circular disks from cardboard:
- Large disk (approx. 10 inches in diameter): This will display the trigonometric ratios.
- Small disk (approx. 6 inches in diameter): This will display the standard angles.
3. Divide the Disks:
- Large Disk:
- Divide it into 6 equal sections using a ruler and compass.
- Label each section with one trigonometric ratio: sinθ\sin \thetasinθ, cosθ\cos \thetacosθ, tanθ\tan \thetatanθ, cscθ\csc \thetacscθ, secθ\sec \thetasecθ, and cotθ\cot \thetacotθ.
- Small Disk:
- Divide it into 5 equal sections to represent the standard angles: 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°.
- Write these angles in their respective sections.
4. Write the Trigonometric Values:
- On the Large Disk, under each ratio section, write the corresponding values for the angles:
- Example for sinθ\sin \thetasinθ:
- 0°: 0
- 30°: 1/2
- 45°: 1/21/\sqrt{2}1/2
- 60°: 3/2\sqrt{3}/23/2
- 90°: 1
- Repeat this for all other ratios (cos\coscos, tan\tantan, etc.).
- Example for sinθ\sin \thetasinθ:
5. Assemble the Rotating Mechanism:
- Stack the small disk on top of the large disk.
- Use a push pin through the center of both disks and into the base. Ensure the disks can rotate freely.
6. Add Labels and Indicators:
- Add a small arrow or indicator on the small disk to point to one angle at a time.
- Add a stationary arrow on the base to indicate which trigonometric ratio is being referenced.
7. Decorate the Model:
- Use colored paper to make the disks visually appealing.
- Add borders, patterns, or other designs to enhance the look.

