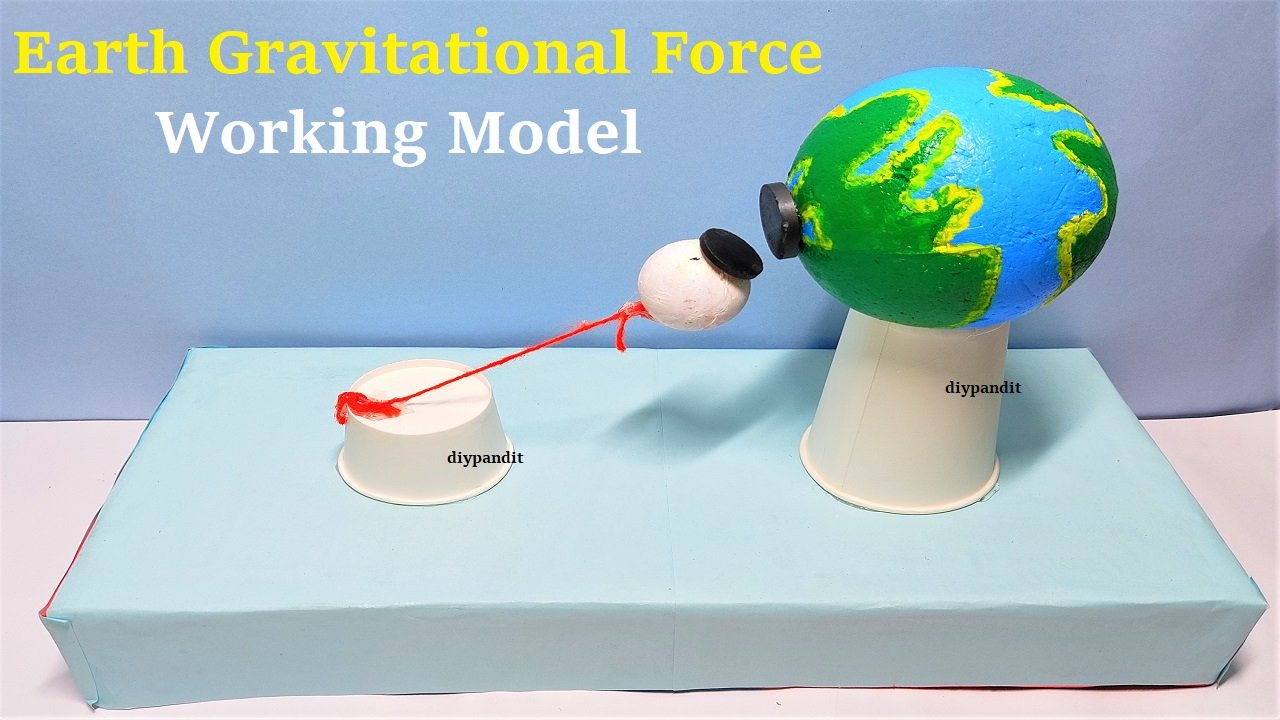
An Earth gravitation working model demonstrates how gravity, a fundamental force, keeps objects on Earth and celestial bodies in orbit. It illustrates how the Earth’s mass pulls objects toward its center, showcasing the universal law of gravitation in an easy-to-understand way.

Key Components of the Model:
- Earth Representation: Use a ball or globe to represent Earth.
- Gravitational Pull: Use elastic bands, strings, or a fabric stretched over a circular frame to simulate the invisible force of gravity pulling objects.
- Objects Representing Mass: Small balls or marbles represent objects influenced by Earth’s gravity.
- Orbiting Objects: A smaller ball attached to a string or circular path around the Earth can represent the Moon or satellites in orbit.
- Support Structure: A sturdy base holds the Earth model and other components in place.
How It Works(Earth gravitation working model):
- Gravity Pulling Objects: Place marbles or small balls on a stretched fabric to demonstrate how they move toward the Earth’s center, simulating gravity pulling objects down.
- Orbits: Swing a smaller ball tied to a string around the Earth model to show how gravity keeps the Moon or satellites in orbit by balancing the force of gravity with the forward motion of the object.
- Falling Objects: Drop an object near the Earth model to explain how gravity accelerates it toward the ground.
Applications and Learning:
- Understanding Gravity: The model explains why objects fall to the ground, why we stay grounded on Earth, and how gravity governs the motion of planets and satellites.
- Educational Insights: It helps students visualize abstract concepts like gravitational pull, mass attraction, and orbital motion.
This hands-on model simplifies the complex concept of gravity, making it accessible for learning and science exhibitions.