Introduction
Green energy, also called renewable or sustainable energy, refers to energy obtained from natural sources that are continuously replenished and cause minimal harm to the environment.
Examples include solar power, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, tidal energy, and biomass.
These sources differ from fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, and natural gas), which take millions of years to form and release large amounts of greenhouse gases when burned.
As the world struggles with the effects of climate change, rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and environmental degradation, the shift toward clean energy is no longer optional—it is essential for the future of human civilisation.
What is Green Energy?
Green energy is defined as energy derived from natural processes that replenish faster than they are consumed. These processes include solar radiation, wind movement, water flow, geothermal heat, biological processes, and ocean tides. The distinguishing characteristics of green energy include:
- Low carbon emissions
- Renewability
- Minimal pollution
- Long-term availability
- Support for ecological balance
In scientific terms, renewable energy sources operate through fundamental natural principles such as the solar cycle, water cycle, atmospheric dynamics, photosynthesis, geothermal heat transfer, and tidal forces generated by gravitational interaction between the Earth, moon, and sun.
Why Green Energy is Important?
1. Environmental Importance
Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), all of which contribute to the greenhouse effect, acid rain, smog, and respiratory illnesses. Green energy significantly reduces these emissions.
2. Combatting Climate Change
Renewable energy sources help limit global warming by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Scientists warn that without drastic emission reduction, global temperatures may rise beyond safe levels.
3. Sustainable Resource Use
Renewable energy does not deplete natural resources. Sunlight, wind, and water flow are constantly available, making green energy a sustainable choice for long-term human development.
4. Economic Growth
The renewable energy industry creates millions of jobs worldwide in manufacturing, installation, research, and maintenance. Countries investing in green energy enjoy long-term economic stability.
5. Energy Security
By reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels, nations can achieve greater energy independence and resilience against price fluctuations.
6. Improved Health
Cleaner air leads to fewer cases of asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, and cardiovascular diseases.
Types of Green Energy
Science students should understand both the principle and mechanism behind each energy source. Below are the major forms of green energy:
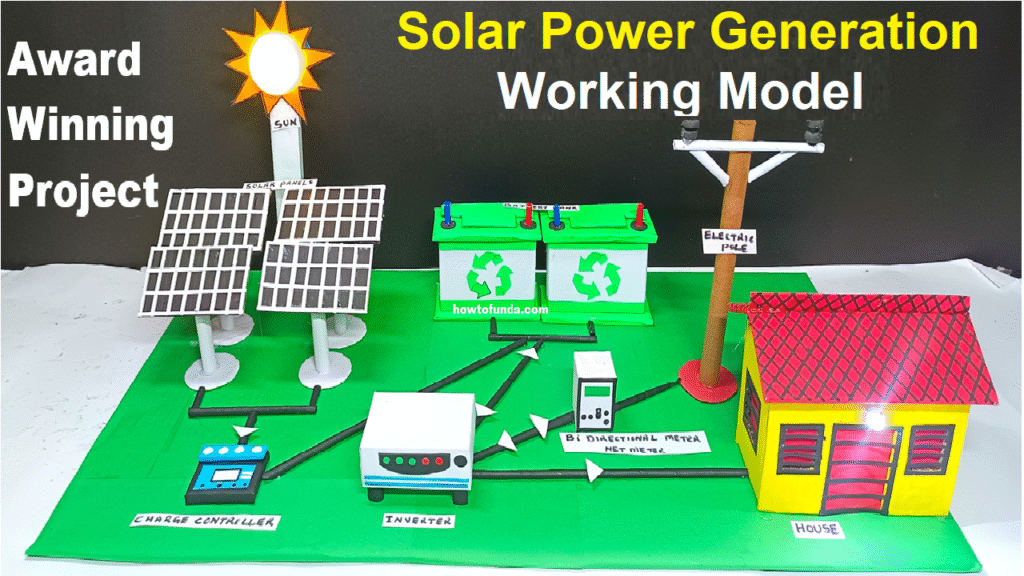
1. Solar Energy
Scientific Principle:
Solar energy is based on photovoltaic effect and solar thermal conversion. When sunlight hits a photovoltaic (PV) cell, electrons are excited and generate an electric current.

Applications:
- Solar panels for electricity
- Solar heaters for water heating
- Solar cookers
- Solar thermal power plants
- Solar desalination
Advantages:
- Abundant and free
- Works even in remote areas
- Reduces electricity bills
Limitations:
- Needs sunlight
- Requires battery storage for night use
2. Wind Energy
Scientific Principle:
Wind turbines convert kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy through generators.

Applications:
- Onshore and offshore wind farms
- Hybrid solar-wind systems
- Powering remote island regions
Advantages:
- Clean and efficient
- Can operate day and night
Limitations:
- Depends on wind speed
- Noise and visual impact
3. Hydropower (Hydroelectric Energy)
Scientific Principle:
Hydropower uses potential energy of stored water and converts it into kinetic energy when released. This movement spins turbines connected to generators.
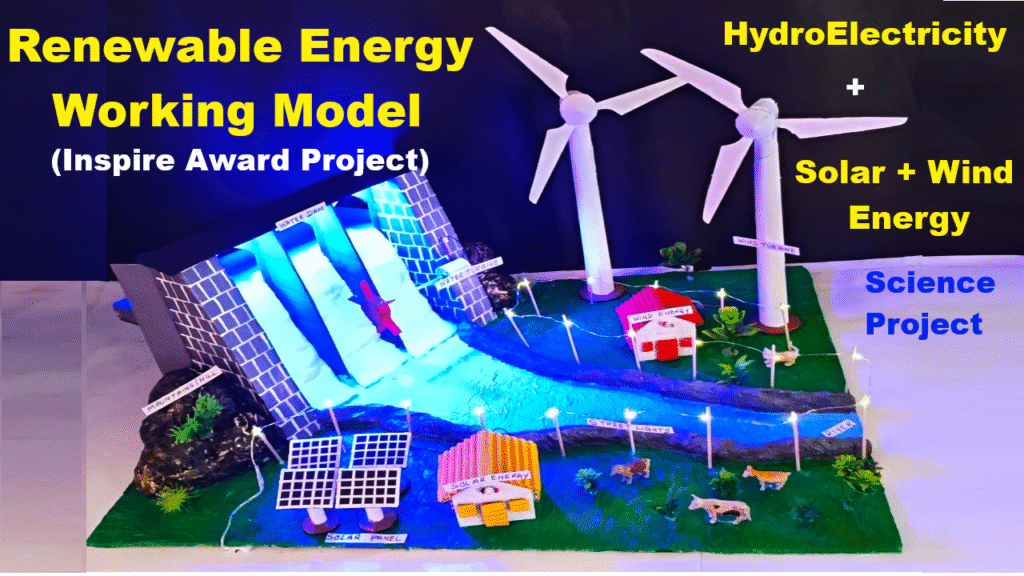
Types:
- Large dam-based plants
- Run-of-the-river systems
- Micro-hydel projects
Advantages:
- Highly efficient
- Provides irrigation and flood control benefits
Limitations:
- High construction cost
- Possible displacement of communities
4. Biomass Energy
Scientific Principle:
Biomass involves chemical energy stored through photosynthesis. Organic matter such as plants, animal waste, and food leftovers can be converted into biogas, biofuels, or heat energy.
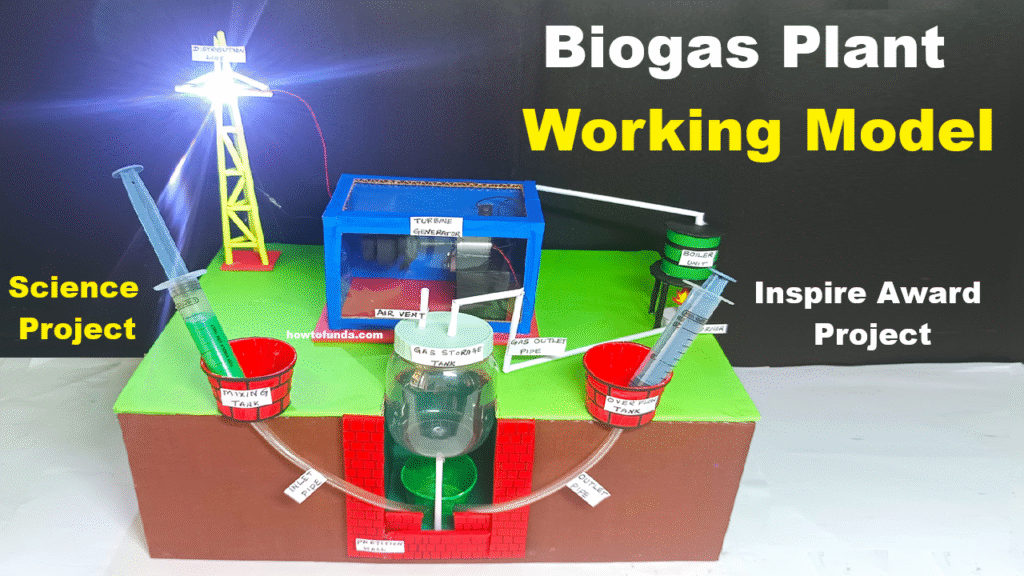
Applications:
- Biogas plants
- Bioethanol and biodiesel
- Biomass power plants
Advantages:
- Utilizes waste materials
- Reduces landfill impact
Limitations:
- Produces small emissions
- Requires careful management
5. Geothermal Energy
Scientific Principle:
Geothermal energy is derived from heat stored beneath the Earth’s crust. Steam and hot water from geothermal reservoirs drive turbines.

Applications:
- Electricity generation
- Direct heating in cold regions
- Industrial drying processes
Advantages:
- Stable power supply
- Minimal environmental impact
Limitations:
- Limited to geologically active areas
- High drilling cost
6. Tidal and Wave Energy
Scientific Principle:
Tidal power depends on gravitational pull of the moon and sun, while wave energy is generated by wind acting on the ocean surface. Turbines and oscillating devices capture this energy.

Advantages:
- Predictable and consistent
- Huge global potential
Limitations:
- High technology cost
- Affects marine ecosystems
Advantages of Green Energy
1. Clean and Pollution-Free
Significantly reduces air and water pollution compared to fossil fuels.
2. Renewable and Sustainable
Sun, wind, water, and geothermal heat are naturally replenished.
3. Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Helps slow global warming and ocean acidification.
4. Job Creation
The renewable energy sector is one of the fastest-growing industries worldwide.
5. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
After installation, maintenance costs are low.
6. Decentralized Energy Production
Rural areas can produce their own electricity.
7. Technological Development
Encourages innovation in energy storage, smart grids, and electric vehicles.
Challenges in Adopting Green Energy
1. High Initial Cost
Solar panels, wind turbines, and hydro plants require significant investment.
2. Storage and Backup Issues
Intermittent sources (solar and wind) require advanced batteries, pumped storage, or hybrid systems.
3. Land Requirements
Large solar farms and wind installations need open areas.
4. Grid Integration
Existing power grids are designed for fossil fuel plants. Modernizing them is expensive.
5. Environmental Concerns
Hydropower dams may submerge forests, and wind farms may affect bird migration.
6. Technological Gaps
Tidal, wave, and geothermal energy need further research.
Green Energy in India
India is rapidly becoming a global renewable energy leader.
Key Statistics:
- India has more than 180 GW of renewable energy capacity (solar, wind, hydro, biomass).
- Target: 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Target: Net-zero emissions by 2070.
Major Initiatives:
- National Solar Mission
- Green Energy Corridor
- Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy
- Rooftop Solar Subsidy Scheme
- Promotion of electric vehicles (EVs)
- Solar parks in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka
- Largest wind farms in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu
India is also working on green hydrogen, floating solar plants, and offshore wind energy, which will revolutionize the energy landscape.
Future of Green Energy
The future of green energy looks extremely promising due to advances in technology and global efforts to reduce carbon emissions.
Emerging Trends:
1. Green Hydrogen
Hydrogen produced through electrolysis using renewable electricity. It can replace diesel, coal, and natural gas in many industries.
2. Next-Generation Batteries
Lithium-ion, solid-state batteries, and hydrogen-based storage will solve the intermittency problem.
3. AI and Smart Grids
Artificial Intelligence will optimize electricity distribution, reduce losses, and balance supply and demand.
4. Electric Vehicles
EV adoption reduces fossil fuel consumption and air pollution in cities.
5. Floating Solar Farms
Panels installed on lakes, reservoirs, and dams increase efficiency by keeping panels cool.
6. Offshore Wind Farms
Wind turbines installed in the ocean generate more power due to strong, stable winds.
7. Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Biomass, biogas, and pyrolysis will convert waste into usable energy, reducing landfill pressure.
Role of Science Students in Promoting Green Energy
Science students can contribute significantly to the green energy revolution through awareness, innovation, and research.
1. Conducting Experiments
- Measuring solar cell efficiency
- Creating low-cost wind turbine prototypes
- Testing biogas production from organic waste
2. Participating in Science Exhibitions
Green energy models (solar tracking system, hydro turbine, smart grid) help raise awareness.
3. Developing DIY Projects
- Solar-powered fan
- Micro-hydel generator
- Windmill working model
4. Research Projects
Students can study renewable energy materials, battery chemistry, and environmental impacts.
5. Awareness Campaigns
Spreading knowledge through seminars, posters, videos, and workshops.
6. Encouraging Sustainable Practices
Promoting recycling, reducing electricity consumption, and supporting eco-friendly technologies.
Conclusion
Green energy is the backbone of a sustainable future. As fossil fuels continue to decline and environmental threats escalate, renewable energy provides a cleaner, safer, and more reliable alternative. For science students, green energy is not just a part of the curriculum but an opportunity to explore scientific principles, develop innovative solutions, and contribute to global environmental protection.
The transition to green energy requires awareness, technical knowledge, innovation, and consistent effort from individuals, industries, and governments. With advancements in solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, biomass, green hydrogen, and energy storage technologies, the world is moving toward a cleaner energy era.
By adopting renewable energy and promoting scientific understanding, we can reduce pollution, slow climate change, and build a future where progress and nature exist in harmony. Green energy is not only a scientific necessity but a commitment to protecting the planet for generations to come.

