Contents:
- Introduction
- What is Biogas?
- Components of a Biogas Plant
- Working Principle of a Biogas Plant
- Types of Biogas Plants
- Feedstock for Biogas Production
- Advantages of Biogas Plants
- Disadvantages and Challenges
- Environmental Impact
- Case Studies
- Steps to Build a Simple Biogas Plant
- Conclusion
- References
1. Introduction
Biogas is a renewable source of energy that is produced by the anaerobic digestion of organic matter.
It is a mixture of gases, primarily methane and carbon dioxide, and can be used for cooking, heating, electricity generation, and even as a vehicle fuel.
This project aims to explore the concept of biogas, the functioning of a biogas plant, and its benefits and challenges.
2. What is Biogas?
Biogas is produced through the decomposition of organic materials such as animal dung, crop residues, kitchen waste, and sewage in the absence of oxygen.
The process involves microbial activity that breaks down the organic matter, resulting in the production of methane, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases.
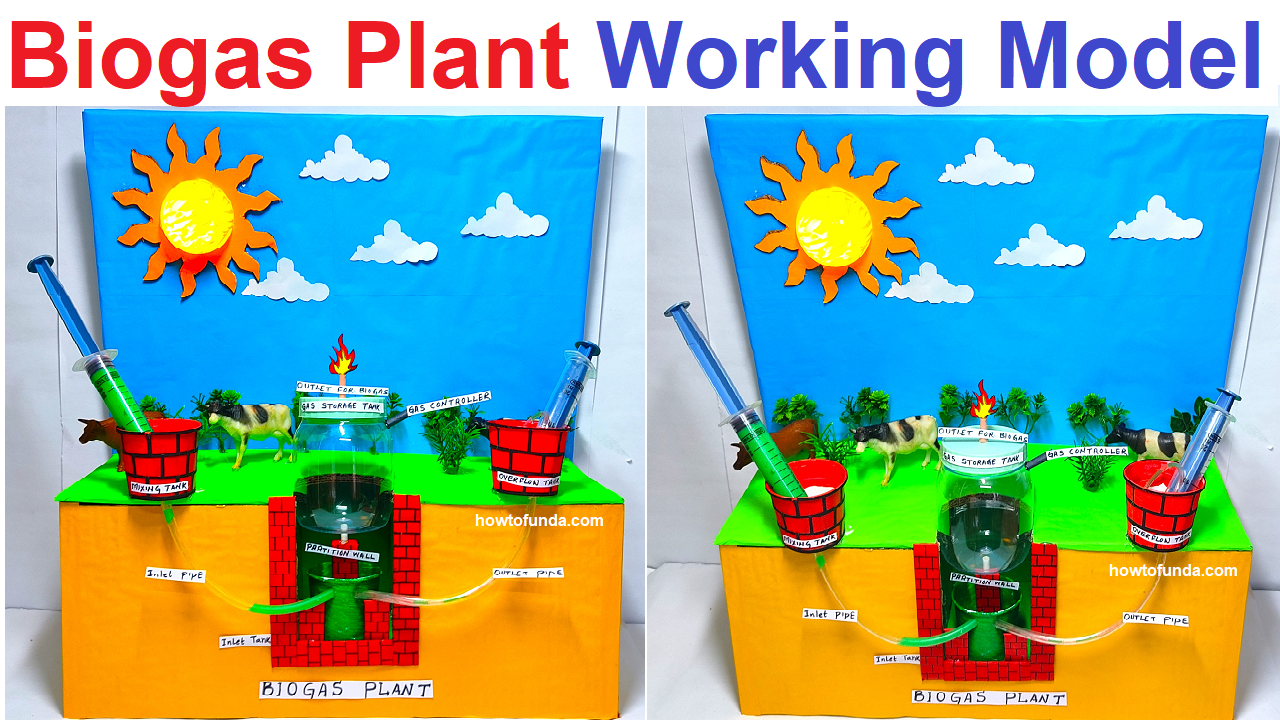
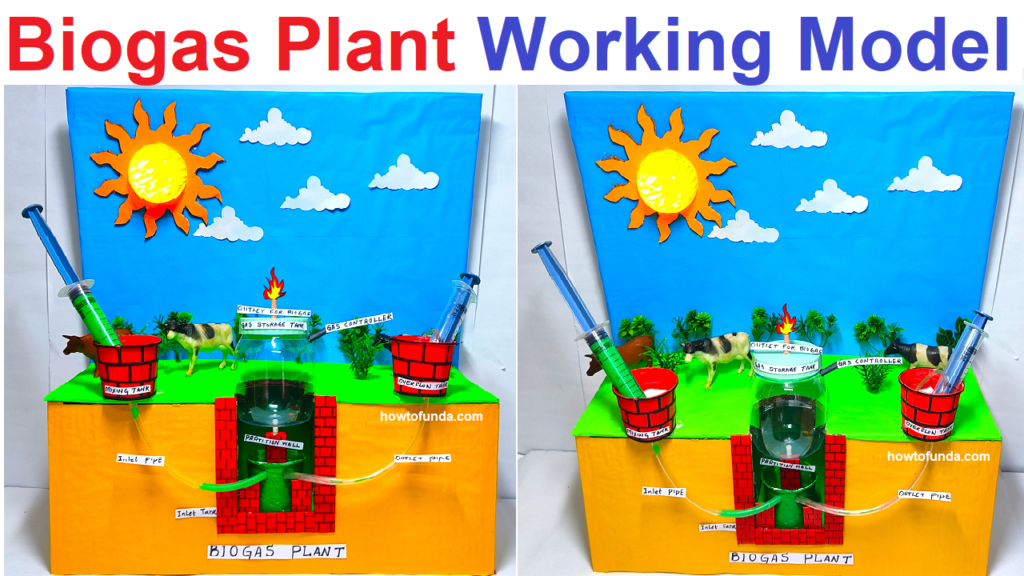
3. Components of a Biogas Plant

A typical biogas plant consists of the following components:
- Inlet Pipe: For feeding organic waste into the digester.
- Digester: An airtight chamber where anaerobic digestion takes place.
- Gas Holder: A storage unit for the biogas produced.
- Outlet Pipe: For removing the digested slurry, which can be used as fertilizer.
- Mixing Tank: Where the feedstock is mixed with water before being fed into the digester.
4. Working Principle of a Biogas Plant
The working of a biogas plant involves the following steps:
- Feeding: Organic waste is mixed with water and fed into the digester through the inlet pipe.
- Anaerobic Digestion: In the digester, microorganisms break down the organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.
- Gas Collection: The biogas rises to the top of the digester and is collected in the gas holder.
- Slurry Removal: The digested slurry is removed through the outlet pipe and can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
5. Types of Biogas Plants
There are several types of biogas plants, including:
- Fixed Dome Biogas Plant: A plant with a fixed, non-movable gas holder, commonly used in rural areas.
- Floating Drum Biogas Plant: A plant with a movable gas holder that rises and falls based on gas production.
- Balloon Type Biogas Plant: A flexible, inflatable digester and gas holder made from rubber or plastic.
- Horizontal Biogas Plant: A plant with a horizontal digester suitable for large-scale biogas production.
6. Feedstock for Biogas Production
Various organic materials can be used as feedstock for biogas production, including:
- Animal dung (cow, pig, poultry, etc.)
- Crop residues (straw, husks, etc.)
- Kitchen waste (vegetable peels, food scraps, etc.)
- Sewage and wastewater
- Industrial organic waste (food processing residues, etc.)
7. Advantages of Biogas Plants
- Renewable Energy Source: Biogas is produced from renewable organic materials, making it a sustainable energy source.
- Waste Management: Biogas plants help in managing and reducing organic waste.
- Eco-Friendly: Biogas production reduces greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Nutrient-Rich Fertilizer: The digested slurry is a valuable fertilizer that enhances soil fertility.
- Energy Independence: Biogas can provide energy independence to rural and remote areas.
8. Disadvantages and Challenges
- Initial Costs: The setup cost of a biogas plant can be high.
- Feedstock Availability: Continuous supply of organic feedstock is essential for consistent biogas production.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure efficient operation.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Biogas production is sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect gas yield.
9. Environmental Impact
Biogas plants have a positive impact on the environment:
- Reduces Greenhouse Gases: Biogas production mitigates methane emissions from organic waste.
- Decreases Pollution: Proper waste management reduces water and soil pollution.
- Sustainable Farming: The use of biogas slurry as fertilizer promotes sustainable agricultural practices.
10. Case Studies
10.1. India
In India, biogas plants have been widely adopted in rural areas, providing a reliable source of energy for cooking and lighting. The National Biogas and Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) supports the installation of biogas plants across the country.
10.2. Germany
Germany has one of the largest biogas industries in the world. The country has invested heavily in biogas technology, with thousands of biogas plants generating electricity and heat from organic waste.
11. Steps to Build a Simple Biogas Plant
Materials Needed:
- A large plastic or metal drum (digester)
- Inlet and outlet pipes
- Gas collection balloon or container
- Mixing tank
- Organic waste (e.g., cow dung, kitchen waste)
Construction Steps:
- Prepare the Digester: Clean the drum and install the inlet and outlet pipes.
- Mix the Feedstock: In the mixing tank, mix the organic waste with water to form a slurry.
- Feed the Digester: Pour the slurry into the digester through the inlet pipe.
- Seal the Digester: Ensure the digester is airtight to allow anaerobic digestion.
- Install the Gas Holder: Connect the gas collection balloon or container to the digester to collect the produced biogas.
- Monitor and Maintain: Regularly check the digester for leaks and feed it with organic waste to maintain biogas production.
12. Conclusion
Biogas plants offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for energy production and waste management.
They play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and supporting agricultural practices.
By understanding the principles and benefits of biogas plants, we can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.