Introduction:
Ladies and gentlemen, esteemed judges, and fellow proponents of sustainable agriculture,
Today, I am excited to present a science project that delves into the transformative world of organic farming.
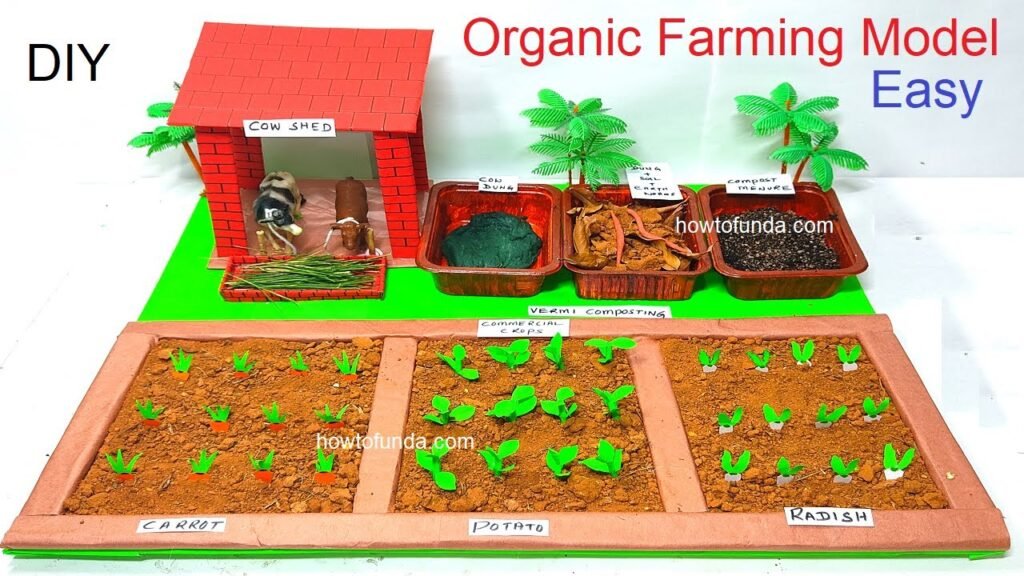
As we gather here at this science exhibition, let us embark on a journey to understand the science behind organic farming, its vital role in addressing agricultural challenges, and the promise it holds for a more sustainable future.
The Urgent Need for Sustainable Agriculture:
Our global population is growing, and with it, the demand for food. Yet, traditional agriculture has often led to environmental degradation, soil depletion, and the excessive use of synthetic chemicals.
In this context, organic farming emerges as a beacon of hope for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to food production.
Exploring Organic Farming:
1. What is Organic Farming?
Organic farming is a holistic approach to agriculture that emphasizes natural and sustainable practices. It rejects synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in favor of natural alternatives, organic matter, and ecological balance.
2. Soil Health and Fertility:
At the heart of organic farming lies the belief that healthy soil is the foundation for robust plant growth. Organic practices focus on enhancing soil fertility through composting, crop rotation, and reduced soil disturbance.
3. Pest and Disease Management:
Organic farming employs integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, such as the use of beneficial insects, trap crops, and resistant plant varieties, to minimize the need for chemical pesticides.
4. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
Organic farms often promote biodiversity by preserving natural habitats and providing refuge for beneficial organisms like pollinators and predators.
5. Sustainable Practices:
Organic farming aims to minimize environmental impact, conserve water, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with the principles of sustainability.
Benefits of Organic Farming:
- Healthier Food: Organic produce is often free from synthetic pesticides and GMOs, making it a healthier choice for consumers.
- Environmental Conservation: Organic farming reduces soil erosion, protects water quality, and supports wildlife, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Organic practices promote long-term sustainability, ensuring that fertile soils and productive farms are preserved for future generations.
- Community Engagement: Organic farming fosters a connection between farmers and their communities, encouraging local and sustainable food systems.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
While organic farming offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Organic yields may be lower in the short term, and the transition from conventional to organic farming can be resource-intensive. However, innovations in organic farming, research in organic pest management, and increased consumer demand for organic products are driving its growth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, organic farming is not just a science project; it is a visionary approach to agriculture that embodies our commitment to a sustainable future. It recognizes the interdependence of human well-being, environmental health, and agricultural practices.
As we continue to explore the science of organic farming, let us celebrate its potential to nourish both our bodies and our planet.
Let us embrace the principles of organic agriculture, support local organic farmers, and work towards a future where healthy, sustainable, and environmentally friendly food production is the norm.
Thank you for joining me on this journey to understand the science and significance of organic farming in shaping a more sustainable and prosperous world.

