Introduction:
Ladies and gentlemen, distinguished guests, and fellow advocates of sustainable agriculture,
Today, I am excited to delve into a groundbreaking agricultural practice that has the potential to transform our food production systems and promote sustainability – hydroponics.
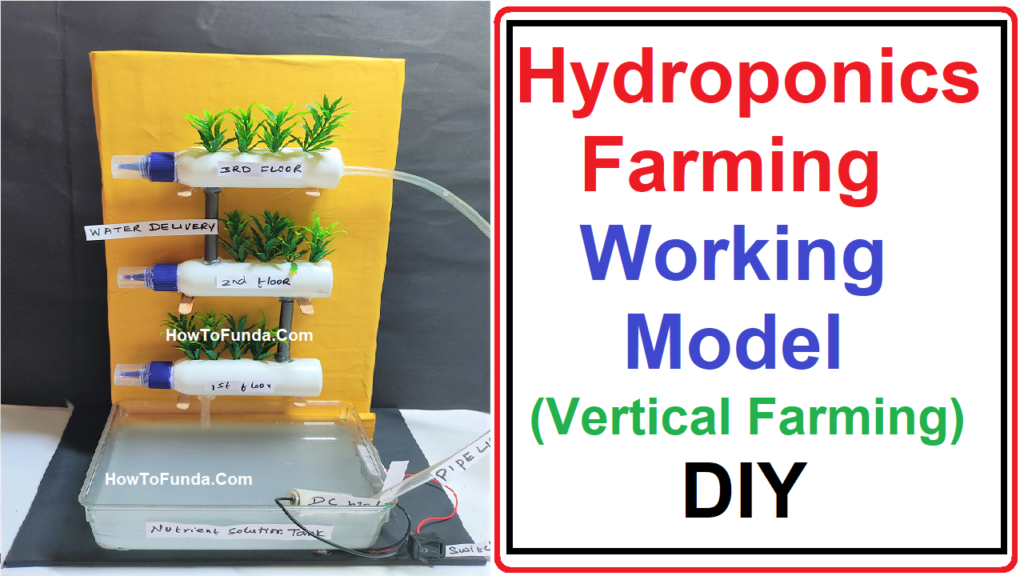
As we gather here at this science exhibition, let us explore the wonders of hydroponics and how it is reshaping the future of farming.
The Agricultural Revolution:
The history of agriculture has witnessed numerous revolutions, from the advent of irrigation to the Green Revolution. Hydroponics represents the next step in this ongoing evolution, offering a novel approach to growing crops without soil.
Hydroponics Unveiled:
At its core, hydroponics is a method of growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, without the need for traditional soil. Instead, plants are grown in various inert mediums such as perlite, coconut coir, or even simply suspended in air with their roots bathed in nutrient solutions.
The Promise of Hydroponics:
Hydroponics holds tremendous promise for addressing some of the most pressing challenges facing modern agriculture:
1. Resource Efficiency: Hydroponic systems use significantly less water than traditional soil-based farming, making them ideal for regions plagued by water scarcity.
2. Controlled Environment: Hydroponic setups allow precise control over environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, optimizing crop growth and quality.
3. Year-Round Cultivation: Hydroponics enables year-round cultivation, reducing our dependence on seasonal factors and providing consistent access to fresh produce.
4. Space Utilization: Vertical hydroponic systems and container farms maximize space utilization, making urban farming and food production more accessible.
5. Reduced Pesticides: Hydroponic systems are less susceptible to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Applications of Hydroponics:
- Urban Farming: Hydroponics can revolutionize urban agriculture by enabling the cultivation of fresh produce in small spaces, such as rooftops and vertical gardens.
- Greenhouses: Hydroponic systems are often integrated into greenhouse operations to extend growing seasons and optimize plant growth.
- Commercial Agriculture: Commercial hydroponic farms produce a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, and even fruits like strawberries.
- Research: Hydroponics is a valuable tool for scientific research, allowing researchers to study plant growth and nutrient uptake under controlled conditions.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
While hydroponics offers immense potential, it is not without challenges. High initial setup costs, energy consumption, and the need for specialized knowledge are hurdles to widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and innovations are continually addressing these challenges and expanding the reach of hydroponics.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hydroponics is not just a revolutionary agricultural practice; it represents a pathway to a more sustainable and food-secure future. It has the power to change the way we grow food, making agriculture more efficient, resource-friendly, and accessible.
As we navigate the challenges of feeding a growing global population and mitigating the impacts of climate change, let us embrace the potential of hydroponics to cultivate a greener, healthier, and more prosperous world for generations to come.
Thank you for joining me on this journey into the world of hydroponics, where innovation meets sustainability in the pursuit of a better tomorrow.

