Objective:
To demonstrate Newton’s Third Law of Motion: “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction” using a simple rocket model powered by a syringe.
Materials Required:
- Syringe (with a plunger)
- Plastic bottle (to create the rocket)
- Rubber stopper (to seal the bottle)
- Plastic tubing (to connect the syringe and rocket)
- Water or air (to launch the rocket)
- Cardboard (for base and stand)
- Glue or tape (for assembly)
- Scissors (to cut materials)
Steps to Build the Newton’s Third Law of Motion Working Model :
- Prepare the Rocket:
- Take a plastic bottle (such as a small soda bottle) to represent the rocket body. This will serve as the launch vehicle.
- Secure a rubber stopper into the bottle’s opening to act as a seal for the rocket. It should fit snugly to prevent air or water from escaping prematurely.
- Set Up the Launching Mechanism:
- Insert a plastic tubing into the rubber stopper. This tubing will serve as the nozzle for the rocket and also connect to the syringe.
- Ensure the tubing is long enough for the syringe to be positioned some distance away from the rocket to allow for safe operation.
- Assemble the Launch System:
- Attach the syringe (without the needle) to the other end of the tubing. This syringe will be used to inject air or water into the rocket.
- Position the syringe in a stable location on the ground or a stand where it can be easily operated.
- Demonstrating the Launch:
- Fill the syringe with air or water (depending on what you prefer to use for propulsion).
- Seal the rocket with the rubber stopper and ensure the tubing is securely connected to both the syringe and the rocket.
- Hold the rocket at a safe angle (with a clear launch path) and quickly press the syringe’s plunger.
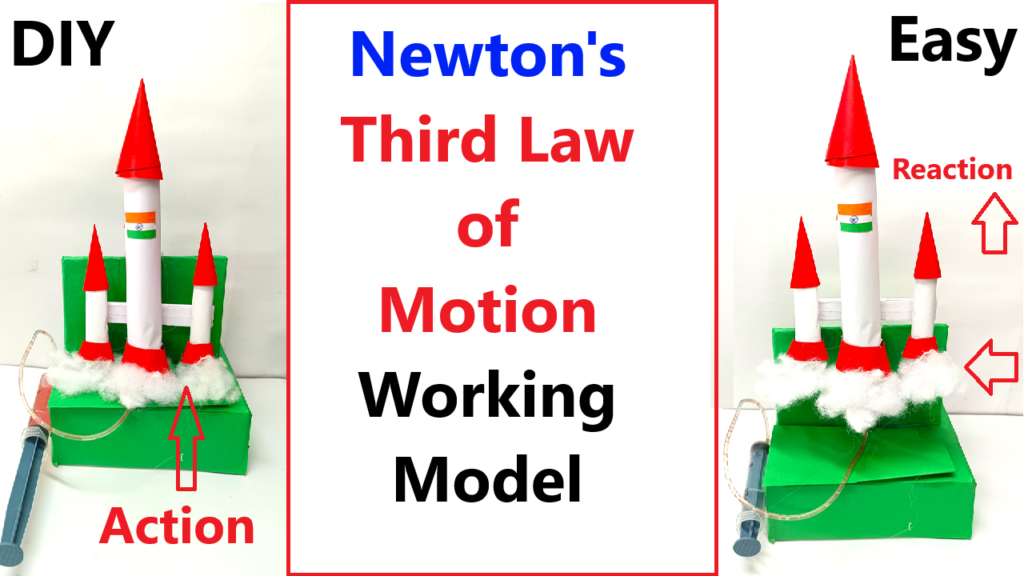
- As the air or water is forced out of the rocket’s nozzle (the tubing), the rocket will move in the opposite direction, illustrating Newton’s Third Law of Motion.
How It Works:
- Action: When you press the plunger of the syringe, air or water is pushed out of the tubing and forced into the rocket.
- Reaction: According to Newton’s Third Law, the rocket experiences an equal and opposite force, causing it to move in the opposite direction of the expelled air or water.
- This action-reaction pair demonstrates how forces work in opposite directions.
Explanation of Newton’s Third Law:
- This working model shows how Newton’s Third Law of Motion operates: The force exerted on the water or air (action) results in an equal and opposite force (reaction) that pushes the rocket upwards.
- The syringe acts as a propulsion system, and the rocket’s movement is a direct result of the force exerted by the expelled fluid.

