Aim / Objective
To demonstrate how mechanical energy can be converted into electrical energy using a DC motor as a generator, and how that generated electricity can power devices (like LED lights).
Materials Required
- 2 small DC motors (3V–9V type)
- 1 9V battery + battery connector
- 1 switch (optional, for control)
- Connecting wires (male-female or bare ends)
- Small rubber belt / thread / gear connection between the two motors
- 2–3 LED lights
- Cardboard base (for fixing motors)
- Glue gun / Fevicol / tape
- Color paper for decoration
- Markers and labels (Input Motor, Generator, LED Output)
Model Construction / Steps
1️⃣ Prepare the Base
- Take a rectangular cardboard sheet as your working base.
- Cover it with color paper for a neat exhibition look.
- Label two zones: “Motor (Input)” and “Generator (Output)”.
2️⃣ Fix the Motors
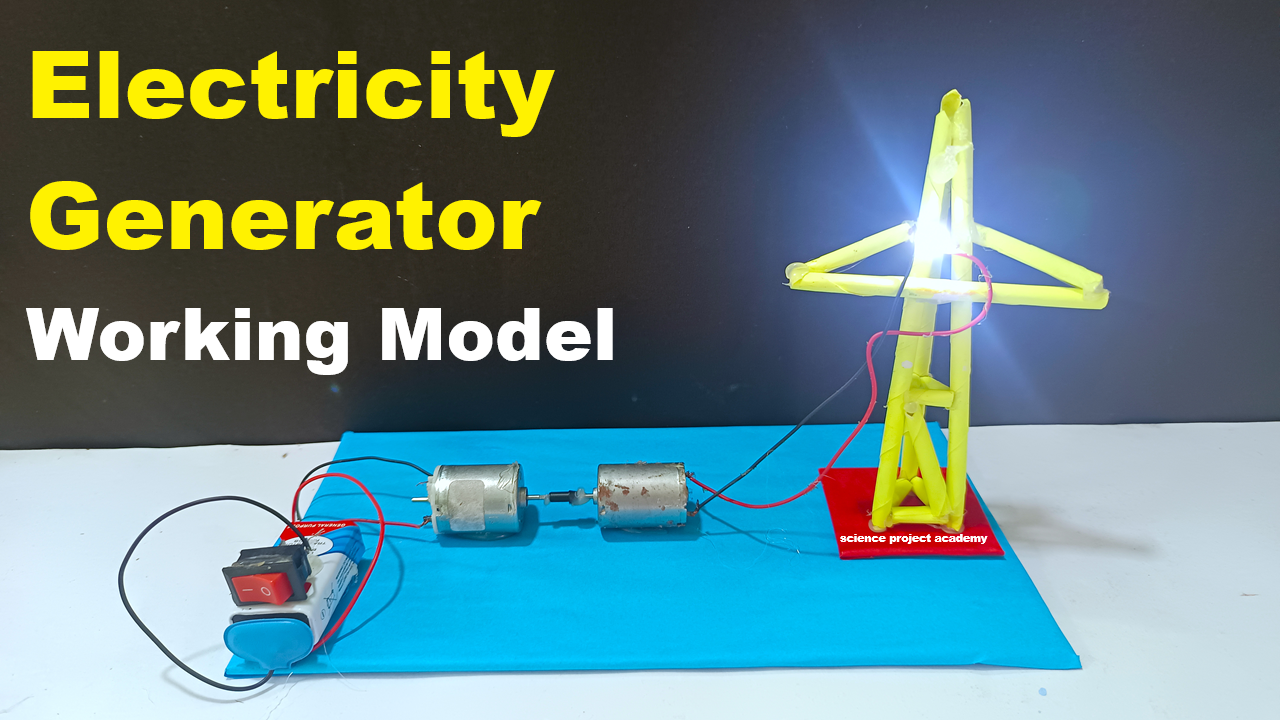
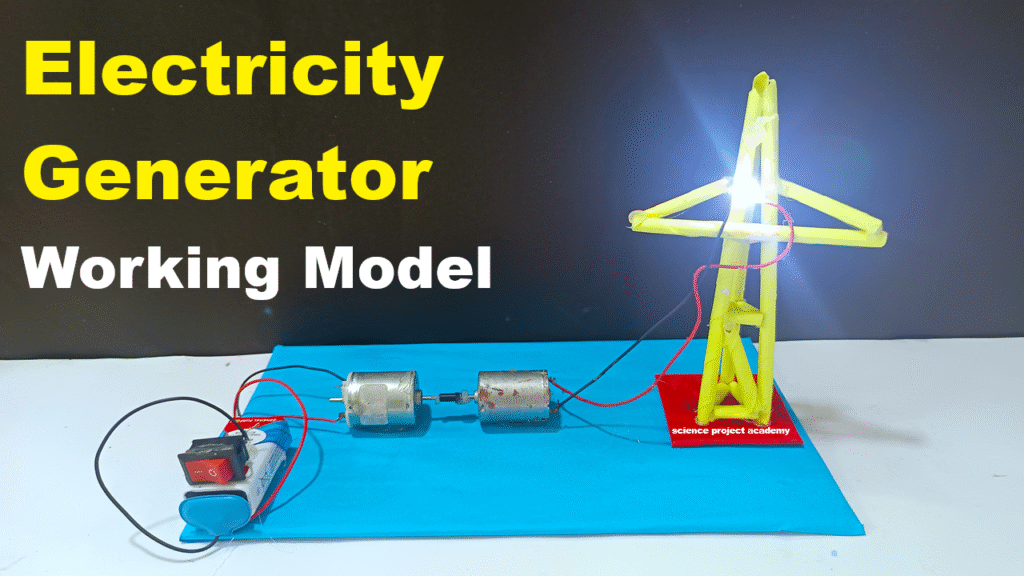
- Glue or tape both DC motors on the base so their shafts face each other.
- Maintain a small gap between the shafts.
- Wrap a rubber band, belt, or thread around both shafts — this will transmit rotation from one motor to another.
Tip: You can also use a gear wheel or fan blade setup if you want visible motion.
3️⃣ Connect the Driving Motor (Input Motor)
- Connect Motor 1 to the 9V battery through a switch.
(Battery + → Motor +, Battery – → Motor –) - This motor will act as the prime mover (it provides mechanical motion).
4️⃣ Connect the Generator Motor (Output Motor)
- Leave Motor 2 unpowered.
- Connect its two output wires to 2 or 3 LEDs in parallel (positive to positive, negative to negative).
- You can add a small resistor (220Ω) if needed for LED protection, but for a short demo, it’s optional.
5️⃣ Test and Observe
- Turn ON the switch → Motor 1 starts rotating, driving Motor 2 through the belt connection.
- As Motor 2 rotates, it starts acting as a generator, producing electricity that lights up the LEDs.
Working Principle
- The first DC motor converts electrical energy (from the 9V battery) into mechanical rotational energy.
- The second DC motor receives that rotation and acts as a generator, converting mechanical energy back into electrical energy.
- The generated electricity lights up the LEDs.
Scientific Explanation
When a DC motor’s shaft is rotated externally, its coil rotates in the magnetic field inside.
According to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, a voltage (EMF) is induced in the coil, generating electric current.
So —
- When you supply current, it acts as a motor.
- When you rotate it externally, it acts as a generator.