Aim / Objective
To demonstrate how conveyor belts are used in industries to transport materials from one place to another efficiently and continuously using a motorized belt system.
Materials Required
- Robo motor (small DC motor)
- 9V battery + battery connector
- Switch (optional, for control)
- Cardboard sheets (for base and frame)
- Color paper (for decoration)
- Rubber band or thick belt (for the conveyor)
- 2 small cylindrical rollers (can use pens, straws, or wooden sticks)
- Glue gun or strong glue
- Tape and scissors
- Small lightweight objects (plastic caps, paper cubes, etc., to demonstrate transport)
- Markers and labels for naming parts
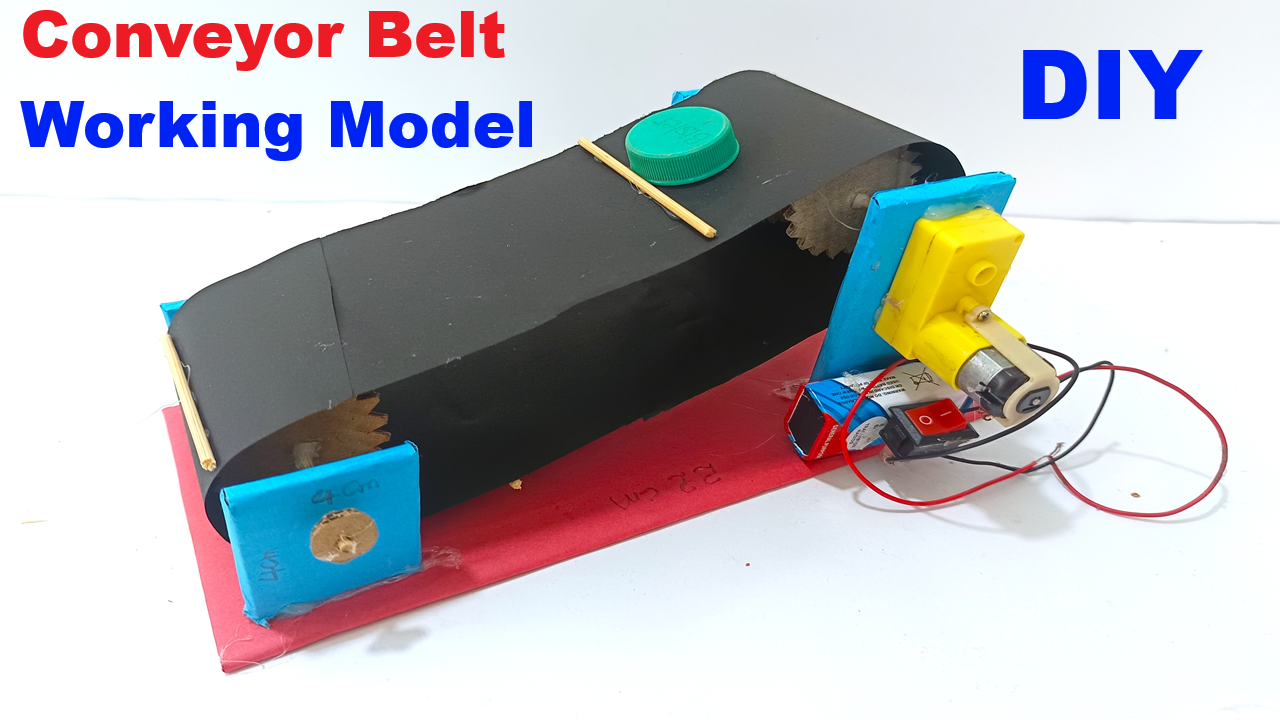
Model Construction / Steps
1️⃣ Base Setup
- Cut a rectangular cardboard base (approx. 30 cm × 15 cm).
- Cover it with color paper for neatness (brown for ground or grey for factory floor).
2️⃣ Roller Frame
- Cut two small cardboard stands (about 5–6 cm tall).
- Attach one roller at the front and one at the back — both should be parallel and able to rotate freely.
(You can use drinking straws as roller holders or insert them through holes in the cardboard stand.)
3️⃣ Attach the Belt
- Use a broad rubber band or strip of thick chart paper looped around both rollers — this becomes your conveyor belt.
- Ensure it’s tight enough to move smoothly when rollers rotate.
4️⃣ Motor Connection
- Fix the robo motor on one side of the stand so that its shaft touches one roller directly (or use a small rubber band as a drive belt between the motor and roller).
- Connect the motor to the 9V battery using wires.
- Add a switch in between if desired to turn the conveyor on/off.
5️⃣ Decoration and Finishing
- Cover the side walls and frame with colored paper.
- Label “Conveyor Belt”, “Motor”, “Rollers”, “Battery”, etc.
- Place small paper boxes or bottle caps on the belt to show movement.
Working Principle
When the 9V battery powers the robo motor, it rotates one of the rollers.
This movement turns the belt loop, causing materials placed on the belt to move forward automatically — just like in factories, airports, and packaging plants.
Scientific Explanation
The model works on the principle of friction and motion transmission:
- The motor converts electrical energy into mechanical rotational energy.
- The roller transmits this motion to the belt via friction.
- The belt’s continuous movement carries objects from one end to another.
Observation
As soon as the motor is switched ON, the belt starts moving smoothly, carrying objects from one side to the other — demonstrating an automated material-handling process.
Conclusion
This model shows how conveyor belts are used in industries for efficient transport of goods, reducing human effort, and speeding up production processes.