Aim / Objective
To test and identify materials as conductors or non-conductors of electricity by checking whether they allow electric current to pass through them.
Materials Required
- Cardboard base (for mounting the setup)
- 9V battery + battery connector
- Switch (on/off)
- LED light (any color)
- Small buzzer or siren module (3V–9V type)
- Connecting wires (with crocodile clips or bare ends)
- Test materials:
- Metal spoon / coin
- Pencil graphite
- Paper
- Wood piece
- Plastic
- Color paper for decoration
- Markers, glue, tape, scissors
Model Construction / Steps
1️⃣ Base Setup
- Take a rectangular cardboard base and cover it with color paper for a neat finish.
- Draw and label sections — “Power Supply”, “Indicator”, “Testing Area”.
2️⃣ Circuit Setup
- Connect the positive terminal of the 9V battery to one terminal of the switch.
- From the switch output, connect to one side of the LED and buzzer (both positive terminals can be connected together).
- Connect the negative side of LED + buzzer to one testing wire (Wire A).
- Connect the other testing wire (Wire B) back to the negative terminal of the battery.
In simple terms:
Battery (+) → Switch → LED & Buzzer → Test Wire A → Material → Test Wire B → Battery (−)
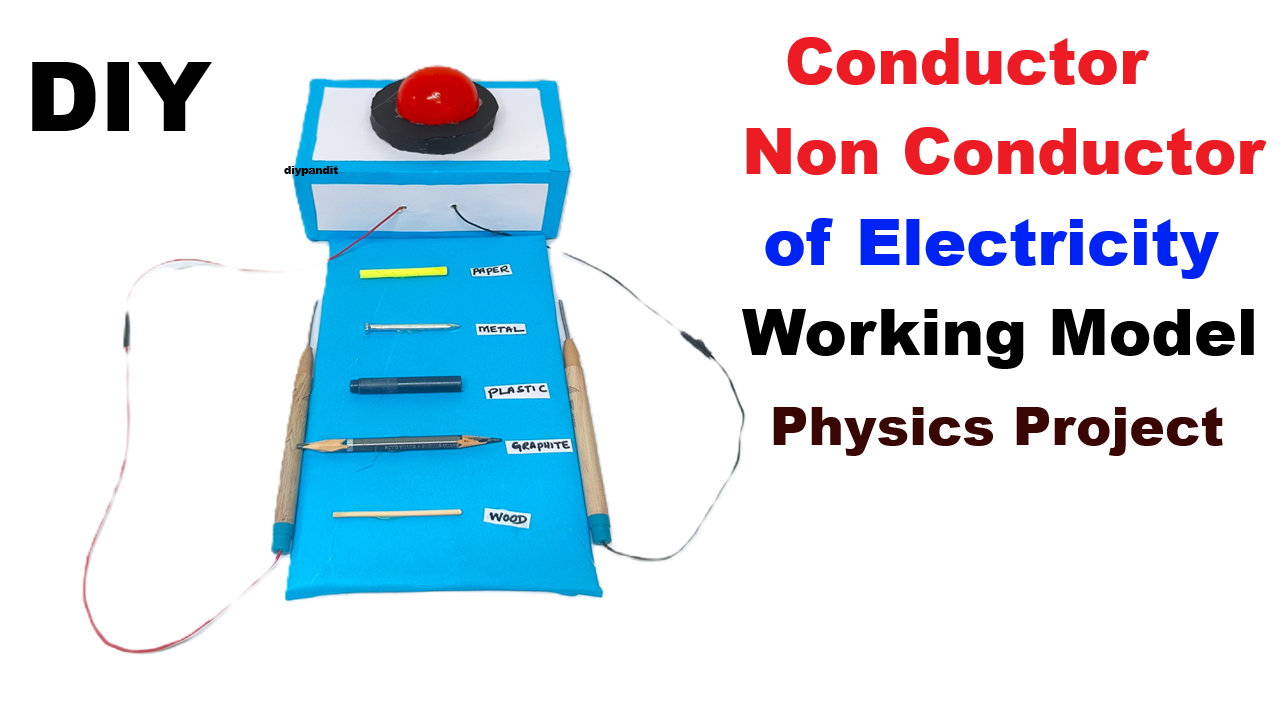
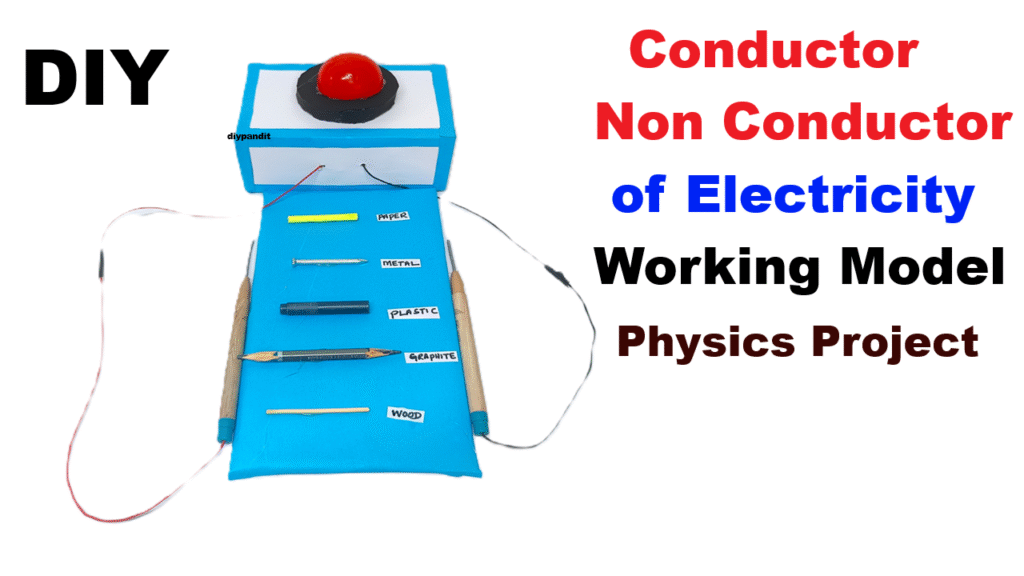
When a conducting material bridges between Wire A and Wire B, the circuit completes, causing LED + buzzer to turn ON.
If non-conducting, circuit remains open → no light, no sound.
3️⃣ Testing Area
- Fix both test wire ends (A & B) on the front side of the base so that you can easily touch the test material between them.
- Label them “Touch Material Here”.
4️⃣ Decoration
- Paste color paper labels:
- “Conductor → Light + Sound ON”
- “Non-Conductor → No Light + No Sound”
- “Electric Tester Model”
- Arrange test materials nearby for demonstration.
Working Principle
Electric current flows only through conductive materials (like metals, graphite).
When the material conducts electricity, it completes the circuit, allowing current to flow → LED glows and buzzer sounds.
If the material is a non-conductor (insulator), the circuit remains open, so no light and no sound occur.
Scientific Explanation
- Conductors (e.g., metal, graphite) have free electrons that allow current to pass easily.
- Non-conductors (insulators) like wood, plastic, and paper do not allow current flow due to tightly bound electrons.
Conclusion
This model demonstrates that electric current flows only through conductors like metals and graphite, while materials like wood, paper, and plastic are non-conductors (insulators).
This principle is widely used in electric testers, switches, and safety devices.