Introduction
In the modern digital world, computer networks play a very important role in communication, data sharing, and information transfer. From schools and offices to banks, hospitals, and the internet, computer networks connect devices and people across the globe. To understand how computers are connected in a network, it is essential to learn about network topology.
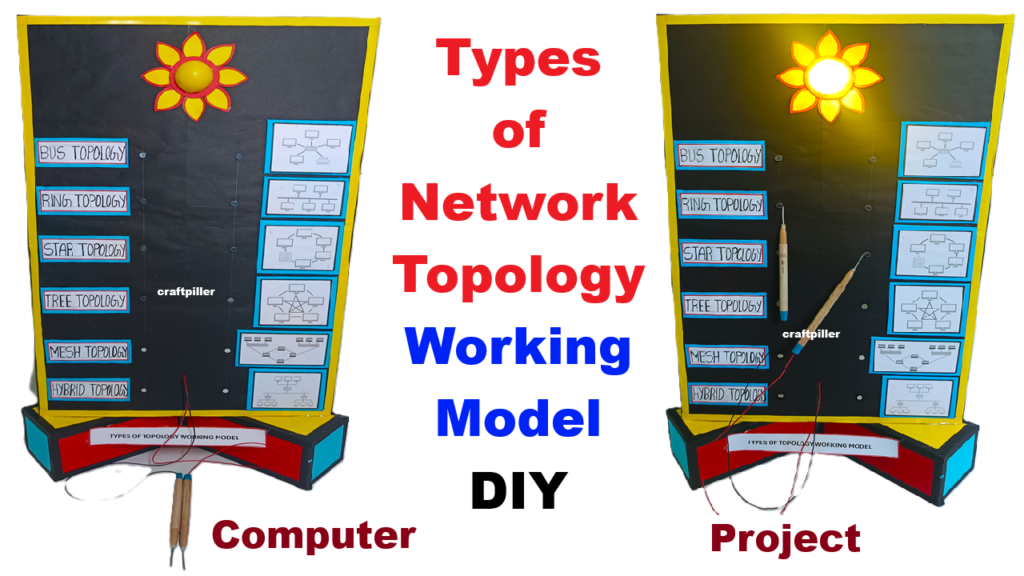
This Types of Computer Network Topology Working Model is designed as a DIY science exhibition project using cardboard and simple materials. The model also includes an interactive quiz board setup, which helps students identify and understand different types of network topologies in a fun and engaging way.
Aim of the Project
The main objectives of this project are:
- To understand the concept of computer networks
- To explain different types of network topologies
- To demonstrate data flow in each topology
- To create an interactive quiz-based learning model
- To improve conceptual clarity through hands-on demonstration
What is Network Topology?
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of computers, cables, and devices in a network. It defines how devices are connected and how data flows between them. Choosing the right topology is important for network performance, cost, scalability, and reliability.
Description of the Working Model
The model is mounted on a large cardboard base and divided into different sections. Each section represents a specific type of network topology. Small computer cut-outs or 3D models made from cardboard represent computers or nodes. Colored wires or paper strips represent network cables.
An interactive quiz board is attached to the model, allowing viewers to guess the topology type and check their answer.
Types of Network Topologies Explained
1. Bus Topology
In bus topology, all computers are connected to a single main cable called the bus.
Working Principle:
- Data travels in both directions along the main cable
- Each computer checks whether the data is meant for it
Advantages:
- Easy to install
- Low cost
Disadvantages:
- Failure of main cable stops the entire network
- Performance decreases with more devices
Applications:
- Small networks and temporary setups
2. Star Topology
In star topology, all computers are connected to a central device such as a hub or switch.
Working Principle:
- Data from one computer goes to the hub
- The hub forwards data to the destination computer
Advantages:
- Easy to manage and troubleshoot
- Failure of one cable does not affect others
Disadvantages:
- Failure of hub stops the network
- Higher cable cost
Applications:
- Schools, offices, and homes
3. Ring Topology
In ring topology, each computer is connected to two other computers, forming a circular ring.
Working Principle:
- Data flows in one direction
- Each computer passes data to the next
Advantages:
- Equal access for all nodes
- No data collision
Disadvantages:
- Failure of one node affects the entire network
- Difficult to troubleshoot
Applications:
- Token-based networks
4. Mesh Topology
In mesh topology, each computer is connected to every other computer.
Working Principle:
- Multiple paths exist for data transmission
- Data chooses the best available path
Advantages:
- Highly reliable
- No single point of failure
Disadvantages:
- Expensive
- Complex installation
Applications:
- Military, banking, and critical systems
5. Tree Topology
Tree topology is a combination of star and bus topology.
Working Principle:
- Multiple star networks connected to a main bus
Advantages:
- Scalable
- Easy to expand
Disadvantages:
- Failure of backbone affects large part of network
Applications:
- Large organizations
6. Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is a combination of two or more topologies.
Working Principle:
- Uses advantages of different topologies
Advantages:
- Flexible and reliable
Disadvantages:
- Costly
- Complex design
Applications:
- Large enterprises and data centers
Quiz Board Setup Explanation
The quiz board is an interactive part of the model. Each topology section has a question such as:
- “Identify this topology”
- “Which topology uses a central hub?”
Students press a button or flip a card to reveal the correct answer. LED lights or answer cards can be used to indicate correct responses. This quiz system:
- Encourages active participation
- Improves memory retention
- Makes learning enjoyable
Educational Importance of the Model
- Makes abstract networking concepts easy to understand
- Encourages hands-on and visual learning
- Suitable for science exhibitions and computer projects
- Enhances communication and presentation skills
Advantages of DIY Cardboard Model
- Low-cost and eco-friendly
- Easy to construct
- Safe for students
- Reusable for classroom teaching
Conclusion
This Types of Computer Network Topology Working Model with Quiz Board Setup is an effective and interactive way to understand computer networking basics. By visually demonstrating bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies, the model helps students grasp complex concepts easily.
The quiz board adds a fun learning element and makes the project stand out in science exhibitions. This project proves that learning computer science concepts can be simple, creative, and enjoyable through DIY models.

