Introduction: Conservation of Energy
Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. It exists in many forms such as mechanical energy, heat energy, light energy, electrical energy, and chemical energy. In our daily life, we constantly observe energy changing from one form to another.
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. This means the total amount of energy in a closed system always remains constant, even though its form may change.
For example, when a ball falls from a height, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Similarly, in an electric bulb, electrical energy is converted into light and heat energy. These transformations clearly demonstrate the conservation of energy.
This principle is very important in science and technology as it helps us understand how machines work, how power is generated, and how energy is used efficiently in our daily lives.
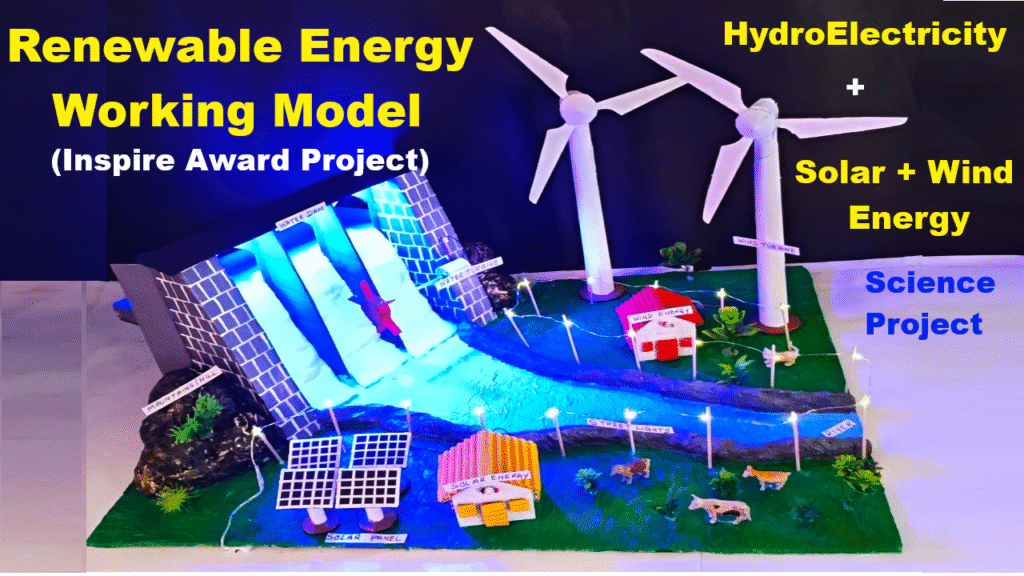
Here are 25 Conservation of Energy working model ideas, suitable for school science exhibitions (Class 8–10). Each model clearly shows how energy changes form but is not destroyed.
Mechanical Energy Models

- Pendulum Energy Model
(Potential ↔ Kinetic energy using a swinging bob) - Roller Coaster Model
(Height → speed → height using balls) - Ball on Inclined Plane
(Gravitational potential → kinetic energy) - Double Ramp Marble Track
(Energy transfer across ramps) - Spring–Mass System
(Elastic potential → kinetic energy) - Newton’s Cradle
(Energy transfer between balls)
Electrical & Mechanical Energy

- Hand Generator LED Model
(Mechanical → electrical → light) - Windmill Power Generator
(Wind → mechanical → electrical) - Water Turbine Generator
(Water flow → electrical energy) - Bicycle Dynamo Model
(Motion → electricity)
Heat & Light Energy Models

- Solar Panel Lighting System
(Solar → electrical → light) - Solar Cooker Model
(Light → heat energy) - Friction Heat Model
(Mechanical → heat) - Thermoelectric Generator (Basic)
(Heat → electrical energy)
Sound Energy Models
- Speaker Vibration Model
(Electrical → sound) - Drum Vibration Model
(Mechanical → sound)
Chemical Energy Models
- Battery-Powered Fan
(Chemical → electrical → mechanical) - Candle Energy Model
(Chemical → heat → light) - Simple Fuel Cell Model (Demo)
(Chemical → electrical)
Mixed Energy Transformation Models

- Chain Reaction Model (Domino + Ball)
(Stored → kinetic → sound) - Lift with Pulley System
(Mechanical → potential energy) - Clockwork Toy Model
(Elastic → mechanical) - Water Lift Using Motor
(Electrical → mechanical → potential) - Magnetic Falling Ball Tube
(Kinetic → heat via eddy currents) - Energy Conversion Park (Mini Exhibition Model)
(Solar, wind, water all in one model)

