Here’s a comprehensive list of Zoology Working Model Ideas suitable for school or college exhibitions — covering topics like human anatomy, animal physiology, ecology, evolution, genetics, and more.
I’ve grouped them into categories to make it easy to choose from.
Human Anatomy & Physiology Models
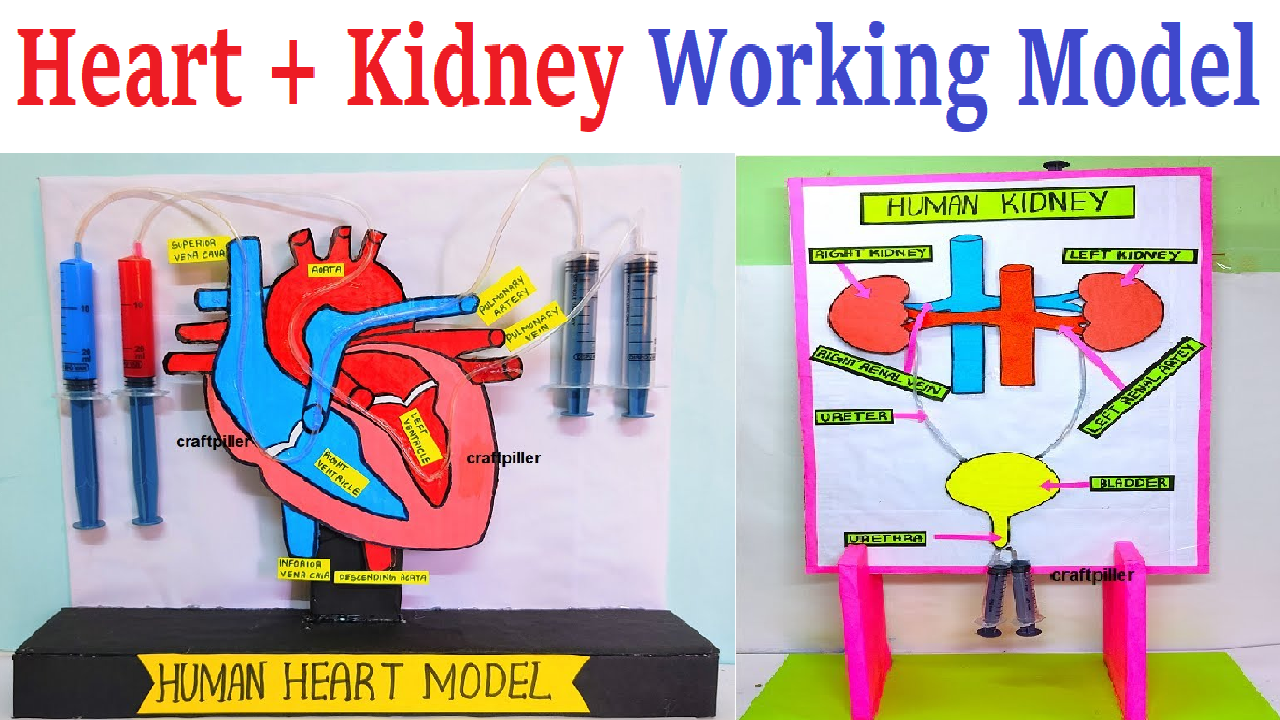
1)Human Heart Working Model (with blood circulation)

The human heart is a muscular organ that works like a pump to circulate blood throughout the body.
It has four chambers –
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
Blood flows through these chambers in a fixed path to ensure the continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to body cells and removal of carbon dioxide and wastes.
Principle:
The working model is based on the principle of double circulation:
- Pulmonary circulation – blood moves from the heart to the lungs and back.
- Systemic circulation – blood moves from the heart to the rest of the body and returns.
This ensures oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood never mix.
2)Human Brain and Nervous System Model (using LED signals)
The nervous system is the control and communication network of the human body.
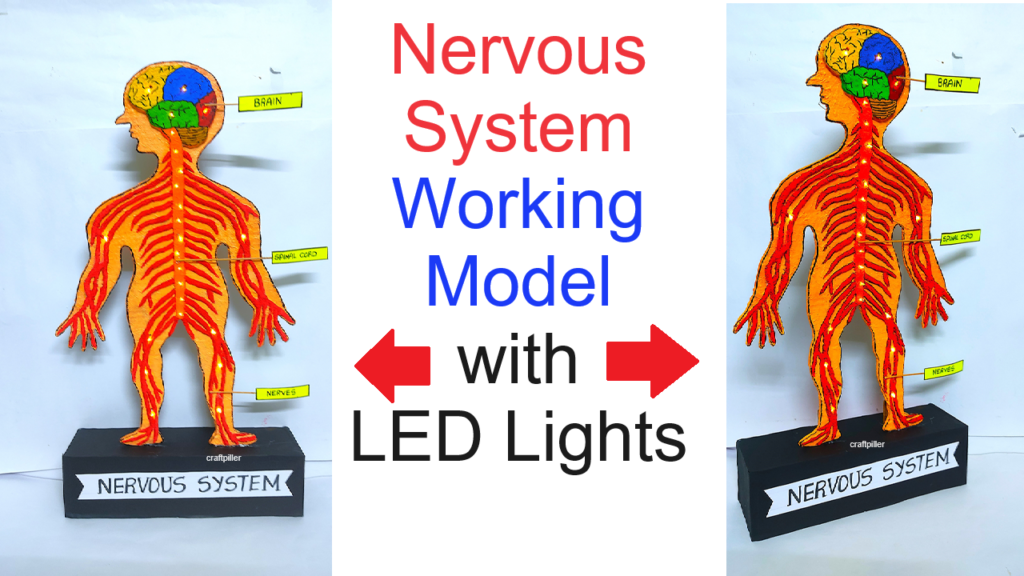
It consists of:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves that connect the CNS to the body
The brain receives information from sensory organs, processes it, and sends messages to muscles and organs to respond appropriately.
3) Human Respiratory System Model (lung balloon setup)
To demonstrate how human lungs expand and contract during inhalation and exhalation, using a simple balloon and bottle setup that mimics the working of the diaphragm and lungs.

The human respiratory system helps us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide.
It consists of organs such as:
- Nose and nasal cavity
- Trachea (windpipe)
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Diaphragm
The lungs act as air sacs where gas exchange takes place, and the diaphragm is a muscle that controls breathing movements.
This model works on the principle of pressure difference inside the chest cavity.
When the diaphragm moves down, the chest volume increases and air enters the lungs (inhalation).
When the diaphragm moves up, chest volume decreases and air is pushed out (exhalation).
4) Human Digestive System Working Model (food journey demo)
The human digestive system breaks down the food we eat into simpler substances that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair.
It consists of several major organs that work together in sequence to process food.
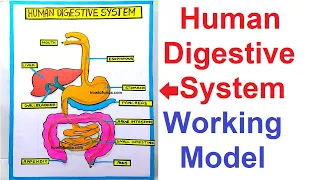
Main Organs of the Digestive System:
- Mouth – Chews food and mixes it with saliva.
- Esophagus – Carries food to the stomach through peristalsis.
- Stomach – Mixes food with gastric juices to form chyme.
- Small Intestine – Digestive enzymes act, and nutrients are absorbed.
- Large Intestine – Absorbs water and forms feces.
- Rectum and Anus – Store and expel waste from the body.
- Accessory Organs: Liver, Pancreas, Gall bladder – help in digestion by producing enzymes and bile.
The model works on the concept of mechanical and chemical digestion, showing how food travels through the digestive organs and how each organ helps in breaking down food step by step.
5) Human Excretory System Model (kidney filtration demo)
To demonstrate how the human excretory system removes waste and excess water from the body through the kidney filtration process, forming urine.

The excretory system is responsible for removing metabolic wastes and maintaining the water–salt balance in our body.
The main organs involved are:
- Kidneys – Filter the blood to remove wastes.
- Ureters – Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Urinary Bladder – Stores urine temporarily.
- Urethra – Expels urine out of the body.
The key function is performed by the nephrons in kidneys — tiny filtration units that purify blood.
This model works on the principle of filtration and reabsorption, similar to how nephrons in the kidneys filter blood to remove urea, salts, and water, and send the clean blood back into circulation.
6) Human Circulatory System Model (pumping red fluid)
The human circulatory system is responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body.

It consists of three main parts:
- Heart – the pumping organ
- Blood Vessels – arteries, veins, and capillaries
- Blood – the transport medium
The heart works like a mechanical pump, maintaining continuous blood flow through a double circulation system:
- Pulmonary circulation (heart ↔ lungs)
- Systemic circulation (heart ↔ body)
The working model demonstrates the pumping action of the heart using red-colored liquid (representing blood) and transparent tubes (representing blood vessels).
When pressure is applied on the heart (pump), the red fluid moves through the circuit, imitating blood circulation.
7) Human Skeleton Moving Parts Model (with joint movement)
To demonstrate the structure of the human skeleton and show how different types of joints enable movement and flexibility in the body.

The human skeleton is the framework of the body, made up of 206 bones that provide support, protection, and movement.
It works together with muscles and joints to help us stand, walk, run, bend, and perform various actions.
The skeleton performs three key functions:
- Support – gives shape to the body.
- Protection – protects internal organs.
- Movement – allows body parts to move using joints.
This working model is based on the mechanical movement of joints (like hinge, ball-and-socket, and pivot joints).
By connecting bones with flexible materials or rods, the model simulates how real human joints move.
8. Human Eye Model (showing focusing mechanism)
To demonstrate the structure of the human eye and explain how light enters the eye, gets focused on the retina, and helps us see.

The human eye is one of the most important sense organs that allows us to see the world around us.
It works like a camera, focusing light to form images. The cornea and lens bend (refract) light rays to focus them on the retina, where the image is formed and sent to the brain through the optic nerve.
The working of the eye is based on the principle of refraction of light — the bending of light rays as they pass through different transparent layers of the eye to form a clear image on the retina.
9. Human Ear Model (vibration to sound transmission)
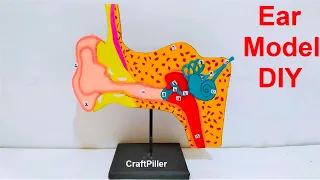
The human ear is a sense organ for hearing and balance.
It detects sound waves and helps maintain body equilibrium.
The ear is divided into three main parts:
- Outer Ear – collects sound waves
- Middle Ear – amplifies sound vibrations
- Inner Ear – converts vibrations into electrical signals
The working of the ear is based on the conversion of sound energy into mechanical energy, and then into electrical impulses, which the brain interprets as sound.
10. Human Skin Model (showing layers and sweat glands)
The skin is the largest organ of the human body, covering the entire surface and protecting internal organs from the external environment.

It acts as a protective barrier, helps regulate temperature, and allows sensation through nerve endings.
The skin also helps in excretion (through sweat) and vitamin D synthesis when exposed to sunlight.
This model demonstrates the layered structure of human skin and how different components like hair follicles, sweat glands, oil glands, and blood vessels function together to protect and regulate the body.
11.Blood Circulation through Heart and Lungs Model
The human circulatory system is a closed-loop system that ensures continuous blood flow between the heart, lungs, and body.

It has two main circuits:
- Pulmonary Circulation – between heart and lungs, for oxygen exchange.
- Systemic Circulation – between heart and rest of the body, for nutrient and oxygen delivery.
This model demonstrates how the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where it becomes oxygenated, and then sends it back to the body.
This model works on the principle of double circulation, showing that blood passes through the heart twice in one complete cycle — once for oxygenation and once for body distribution.
12. Neuron Structure and Impulse Transmission Model
The neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It is responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals.

This model helps visualize how an impulse travels along a neuron and from one neuron to another through a synapse.
The model works on the principle of electrochemical signal transmission, showing how impulses travel in one direction along the neuron — from dendrites to axon terminals — and how neurons communicate across synaptic gaps.
13. Reflex Action Demonstration (spinal cord reflex arc)
A reflex action is a rapid and automatic response of the body to a stimulus.

For example:
- Pulling your hand away from a hot object
- Blinking when something comes near your eyes
- Jerking your leg when the doctor taps your knee
This model shows how the reflex arc pathway helps the body react instantly to protect itself from harm, even before the brain becomes aware.
The reflex arc is the pathway through which nerve impulses travel during a reflex action.
It involves receptors, sensory neurons, spinal cord (interneuron), motor neurons, and effectors.
The message bypasses the brain for a faster reaction.
14. Human Reproductive System Model (female)
The female reproductive system is a group of organs responsible for producing egg cells (ova), allowing fertilization, and nurturing a developing fetus until birth.

It plays a vital role in human reproduction, hormone regulation, and menstrual cycles.
This model helps to visualize the internal reproductive organs and understand their functions and interconnections.
Main Parts of the Female Reproductive System:
- Ovaries – Two small, oval-shaped glands located on either side of the uterus.
- Function: Produce ova (egg cells) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts) – Thin tubes connecting the ovaries to the uterus.
- Function: Transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
- Fertilization usually occurs here when a sperm meets the egg.
- Uterus (Womb) – A pear-shaped muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity.
- Function: Receives the fertilized egg, supports embryo and fetal development, and contracts during childbirth to deliver the baby.
- Endometrium – The inner lining of the uterus.
- Function: Thickens each month in preparation for a possible pregnancy and sheds during menstruation if no fertilization occurs.
- Cervix – The narrow, lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
- Function: Acts as a gateway between the uterus and vagina; expands during childbirth.
- Vagina (Birth Canal) – A muscular passage leading from the cervix to the external body.
- Function: Serves as the exit for menstrual flow, receives sperm during reproduction, and acts as the birth canal during delivery.
15 . DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis Model
All living organisms inherit traits through DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) — the molecule that carries genetic instructions for growth, reproduction, and functioning.

This model visually represents two major processes:
- DNA Replication – Copying of DNA before cell division.
- Protein Synthesis – Formation of proteins from the DNA code through transcription and translation.
It helps students understand how genetic information stored in DNA is decoded into proteins, which perform vital roles in every cell.
The model is based on the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology:
DNA → RNA → Protein
It explains that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA (transcription) and from RNA to protein (translation).