A Thermal Energy Generator converts heat energy into electrical energy. One simple and popular method uses a Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) module. TEC is a small device that can generate electricity when there is a temperature difference between its two sides.
In this setup, one side of the TEC is kept hot (using a candle, solar heat, or a hot plate), and the other side is kept cool. The temperature difference makes the electrons move, generating a small electric current. This current can be used to power small devices like LEDs, fans, or sensors.
Thermal energy generators with TEC are eco-friendly, portable, and useful in areas where heat is available but electricity is not. They show how renewable energy and science can be used in practical ways.
How To Make Thermal Energy Generator
Here’s a creative and practical Thermal Energy Generator (Heat to Electricity) Working Model idea using a TEC (Thermoelectric Cooler) to power a DC motor (for rotation) and a buzzer (for sound). This is ideal for science exhibitions, especially under energy conversion themes.
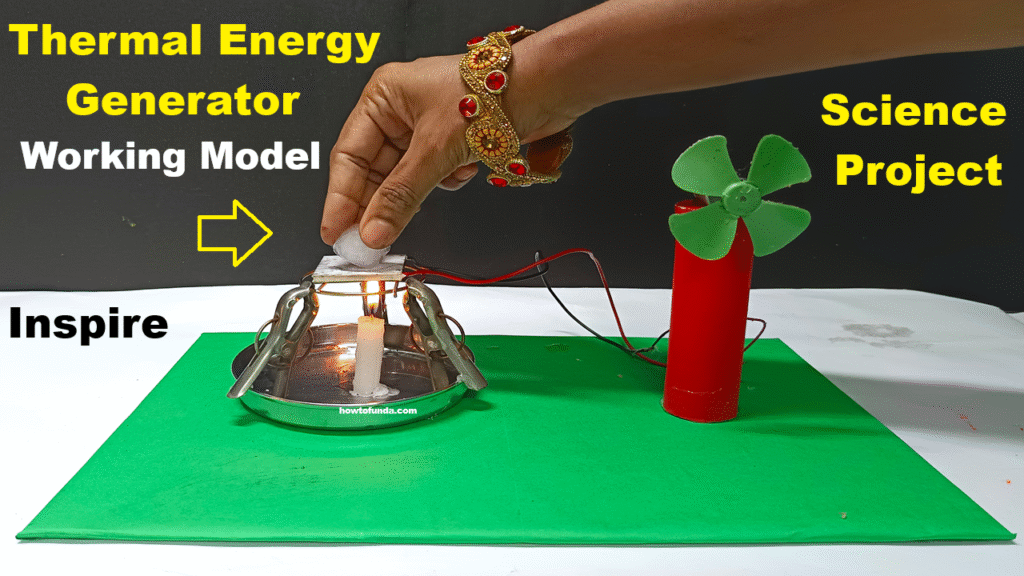
This model demonstrates the conversion of thermal energy directly into electrical energy using a thermoelectric module.
The TEC module generates voltage when there’s a temperature difference between its two sides.
This electricity powers a DC motor and a buzzer, showing how waste heat from industries, solar heat, or even body heat can be reused for powering small devices — a step towards sustainable and renewable energy solutions.”
Materials Required:
- 1x TEC (Thermoelectric Cooler) module – e.g., TEC1-12706
- 1x DC Motor (3–6V)
- 1x Buzzer (3V or 5V)
- 1x Heat source (like a metal spoon with candle or hot water in a metal container)
- 1x Cooling source (aluminum heatsink, wet cloth, or ice pack)
- Wires & switches
- Cardboard stand/base
- LED (optional, to show current flow)
How It Works (Concept):
- TEC modules work on the Seebeck effect — they generate electricity when there’s a temperature difference between their two sides.
- The hot side (exposed to heat) and cold side (with cooling) create voltage.
- This voltage is used to:
- Rotate a DC motor (shows mechanical energy).
- Activate a buzzer (shows sound energy).
- (Optional) Light up an LED.
Video Steps to Build the Working Model:
- Mount the TEC module on a flat surface (cardboard or wooden base).
- Attach a heatsink or wet sponge to the cold side.
- Expose the hot side to a heat source – candle, hot cup, or hot metal.
- Connect the TEC output wires to:
- DC Motor (fan blade can be added to show rotation).
- Buzzer in parallel.
- Optional: Add a switch to control output.
- As heat is applied, the TEC will generate voltage, causing:
- Motor to rotate
- Buzzer to buzz
Output Observation:
- As soon as a sufficient temperature difference is reached:
- Motor starts spinning (thermal to mechanical energy).
- Buzzer makes sound (thermal to sound energy).
- You can explain how no batteries are used – only heat energy.

