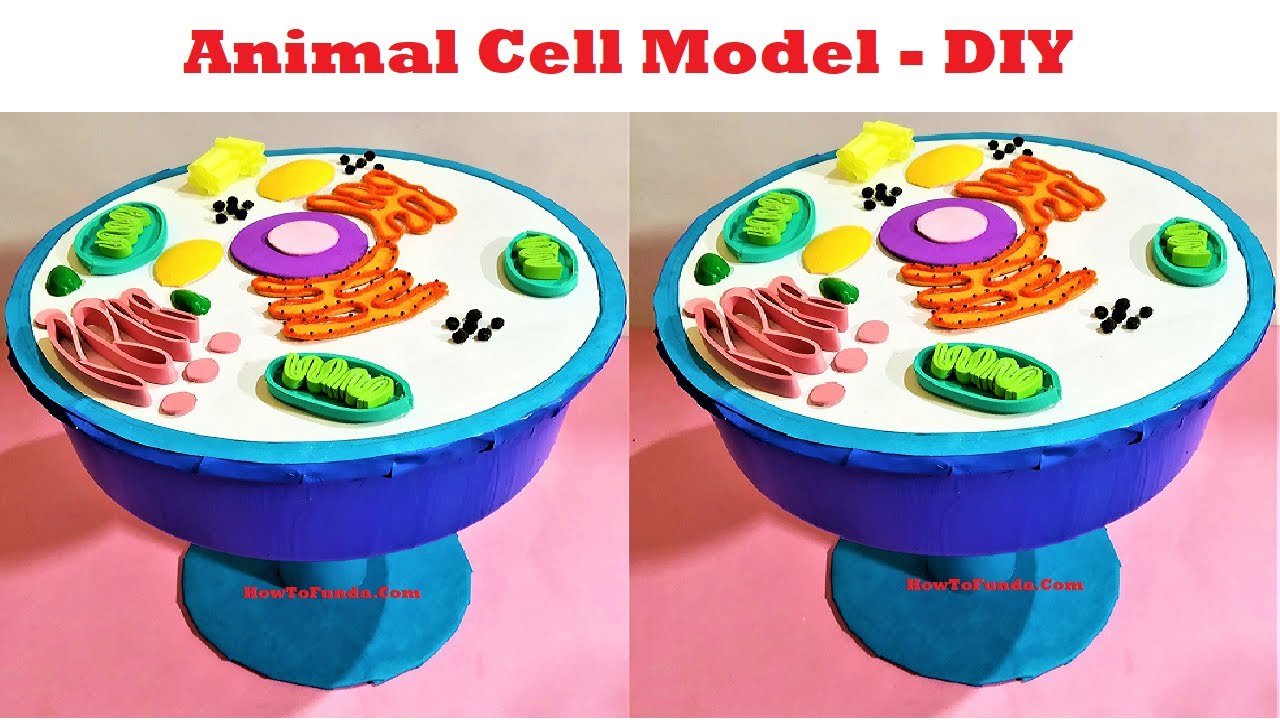
Overview:
Every living organism is made up of cells, and animal cells are remarkable in their complexity and diversity of functions.
Our animal cell model will provide a three-dimensional representation of an animal cell, allowing us to visualize and understand its various organelles and their roles in cellular processes.
Components of the Animal Cell Model:
Before we delve into the details, let’s familiarize ourselves with the components of our animal cell model:
- Cell Membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that controls what enters and exits the cell.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) and governing cell activities.
- Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance that fills the cell and houses organelles.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouses of the cell, responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell.
- Ribosomes: The site of protein synthesis, where amino acids are assembled into proteins.
- Lysosomes: Digestive organelles that break down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Vacuoles: Storage organelles that store water, nutrients, and waste products.
- Centrioles (in animal cells): Structures involved in cell division and the formation of spindle fibers.
Demonstration of Animal Cell Model:
- Cell Membrane and Cytoplasm:
- The cell membrane forms the boundary of the cell, while the cytoplasm fills the cell’s interior.
- Point out the cell membrane and the transparent gel-like substance representing the cytoplasm.
- Nucleus and Genetic Material:
- The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, which contains instructions for cellular activities.
- Highlight the nucleus and explain its role as the control center of the cell.
- Organelles and Their Functions:
- Each organelle performs specific functions vital for the cell’s survival and functioning.
- Point out and explain the functions of mitochondria, ER, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles using visual aids or labels.
- Cellular Processes:
- These organelles work together to carry out essential cellular processes such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste disposal.
- Discuss how mitochondria produce energy, ribosomes synthesize proteins, and lysosomes break down waste materials.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, our animal cell model provides a glimpse into the intricate world of cellular biology. Through this exhibit, we hope to inspire curiosity and appreciation for the remarkable complexity of life at the cellular level.