4 biology science project model making for science exhibition – diy – simple and easy | craftpiller
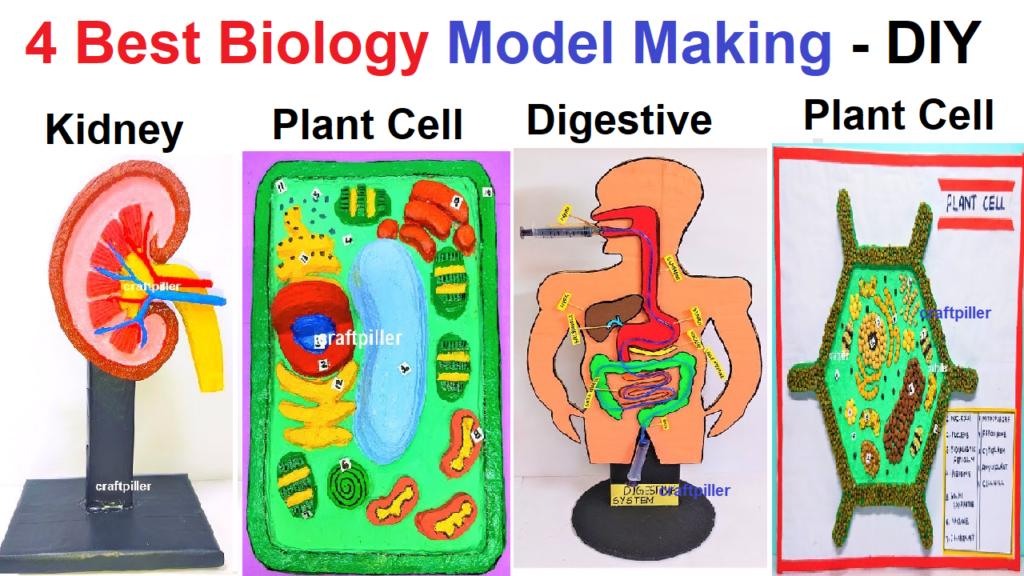
Kidney: The kidney is a vital organ in the human body that plays a key role in the urinary system. Each person typically has two kidneys, located on either side of the spine, below the ribcage. The kidneys are responsible for several essential functions such as Filtration and Excretion, Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Acid-Base Balance, Blood Pressure Regulation, Red Blood Cell Production
Plant Cell: Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane. Plant cells have several unique structures and features:
- Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, which provides structural support and protection.
- Cell Membrane: The cell membrane surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Nucleus: The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance inside the cell where various cellular processes occur.
- Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are organelles responsible for photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into chemical energy (glucose) for the plant’s use.
- Vacuole: Plant cells often have a large central vacuole filled with cell sap, which helps maintain cell turgor pressure and stores nutrients and waste products.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles responsible for cellular respiration.
Plant cells are responsible for carrying out all the processes necessary for plant growth, development, and survival. They can vary in shape and size depending on the specific type of plant.
Digestive System: The digestive system is a complex system responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body. It involves several organs and structures:
- Mouth: The process of digestion begins in the mouth, where food is broken down mechanically by chewing and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that start the digestion of carbohydrates.
- Esophagus: The esophagus is a muscular tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach through peristaltic contractions.
- Stomach: In the stomach, food is mixed with gastric juices containing enzymes and hydrochloric acid. This acidic environment helps break down proteins.
- Small Intestine: The majority of digestion and nutrient absorption occur in the small intestine. Enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver aid in breaking down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Liver: The liver plays a crucial role in the digestive system by producing bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to help emulsify fats.
- Pancreas: The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that are released into the small intestine to further break down nutrients.
- Large Intestine: The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the undigested food, forming feces, which are eventually eliminated from the body through the rectum and anus.
The digestive system ensures that nutrients are absorbed from the food we eat, providing the body with energy and essential substances for growth, repair, and maintenance. Proper nutrition and a healthy digestive system are essential for overall health and well-being.
#biologyproject #scienceproject #modelmaking #scienceexhibition #modelmaking #craftpiller #biologyproject

