1. What is the brain?
- Answer: The brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, responsible for processing information, controlling body functions, and enabling cognitive activities.
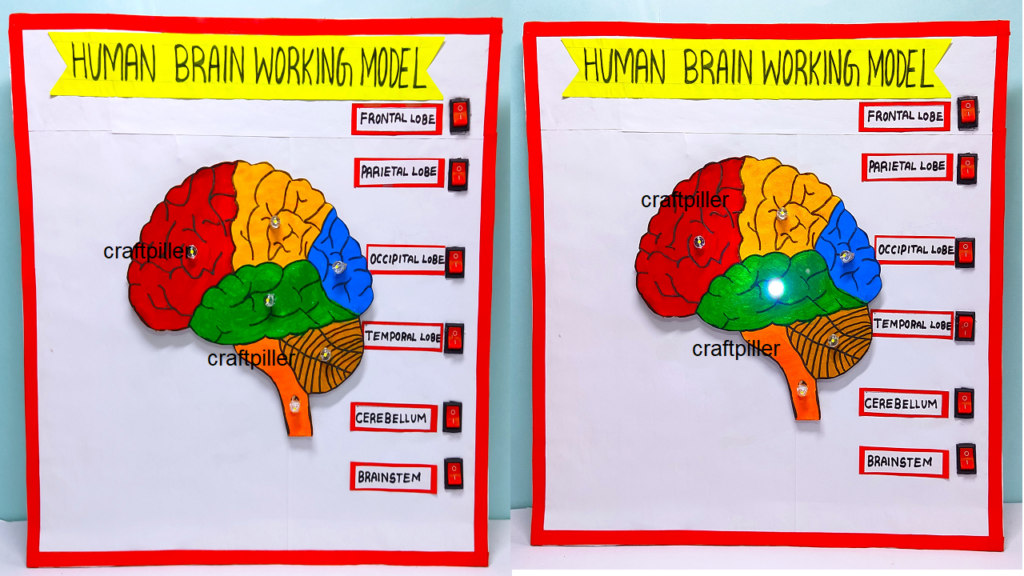
2. How much does the human brain weigh?
- Answer: The average adult human brain weighs about 3 pounds or 1.4 kilograms.
3. What are the main parts of the brain?
- Answer: The brain consists of three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
4. What is the function of the cerebrum?
- Answer: The cerebrum is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, learning, memory, and voluntary movements.
5. What does the cerebellum control?
- Answer: The cerebellum is primarily involved in the coordination of voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
6. What is the role of the brainstem?
- Answer: The brainstem regulates basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure. It also serves as a pathway for information to and from the brain.
7. How is the brain protected?
- Answer: The brain is protected by the skull, a bony structure that surrounds and provides a hard barrier to shield the brain from external impacts.
8. What is the blood-brain barrier?
- Answer: The blood-brain barrier is a protective barrier that separates the blood circulation from the brain tissue, preventing harmful substances from easily entering the brain.
9. How does the brain receive oxygen and nutrients?
- Answer: The brain receives oxygen and nutrients through the blood vessels, including arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the brain.
10. What are neurons?
Answer: Neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system that transmit electrical and chemical signals, allowing communication within the brain and throughout the body.
11. How do neurons communicate with each other?
Answer: Neurons communicate through electrical impulses and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. When one neuron sends a signal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters that affect neighboring neurons.
12. What is the role of dendrites in neurons?
Answer: Dendrites are branch-like extensions of neurons that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them toward the cell body.
13. What is the function of the axon in a neuron?
Answer: The axon is a long, slender projection of a neuron that carries electrical impulses away from the cell body, transmitting signals to other neurons or cells.
14. What is a synapse?
Answer: A synapse is a small gap or junction between two neurons where the transmission of signals occurs through the release and reception of neurotransmitters.
15. How does the brain control voluntary movements?
Answer: The brain controls voluntary movements through a complex network of motor neurons and the coordination of muscle contractions.
16. What is the role of the frontal lobe in the brain?
Answer: The frontal lobe is responsible for functions such as decision-making, personality, voluntary movement, and higher cognitive processes.
17. How does the brain process sensory information?
Answer: The brain processes sensory information by receiving signals from sensory organs (e.g., eyes, ears) and interpreting them in specialized regions.
18. What is the role of the hippocampus in the brain?
Answer: The hippocampus is involved in the formation of new memories and is crucial for learning and spatial navigation.
19. How does sleep affect the brain?
Answer: Sleep is essential for the brain’s overall health, memory consolidation, and cognitive functions. It allows the brain to rest and rejuvenate.
20. What is the function of the amygdala?
Answer: The amygdala plays a key role in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure responses.
21. What are brain waves?
Answer: Brain waves are patterns of electrical activity generated by the neurons in the brain. They can be observed and measured using electroencephalography (EEG).
22. How does stress impact the brain?
Answer: Chronic stress can negatively impact the brain, affecting memory, cognitive functions, and increasing the risk of mental health disorders.
23. Can the brain regenerate cells?
Answer: Yes, the brain can generate new neurons in a process called neurogenesis, particularly in certain regions like the hippocampus.
24. What is the significance of the prefrontal cortex?
Answer: The prefrontal cortex, located in the frontal lobe, is associated with executive functions, including decision-making, problem-solving, and impulse control.
25. How does exercise benefit the brain?
Answer: Exercise improves blood flow to the brain, stimulates the release of neurotransmitters, and promotes the growth of new neurons, contributing to better cognitive function and mental health.

