1. What is a parallel circuit?
- Answer: A parallel circuit is an electric circuit in which the components (resistors, bulbs, etc.) are connected in separate branches, and the current can flow through each component simultaneously.
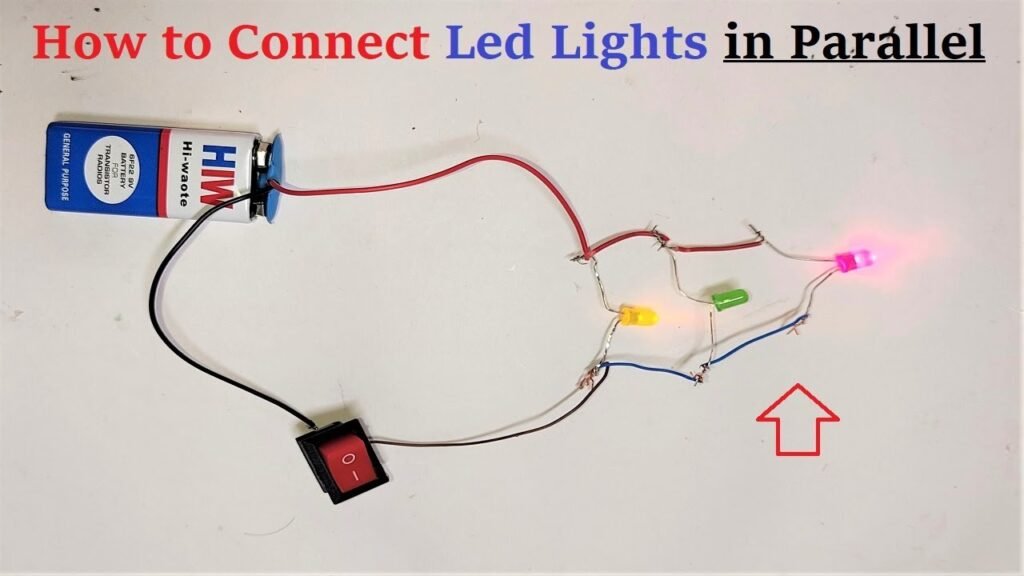
2. How does the current flow in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: In a parallel circuit, the current splits at junctions, and each branch carries a portion of the total current. The current in each branch is independent of the others.
3. What happens to the voltage in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: In a parallel circuit, each component has the same voltage across its terminals, equal to the total voltage of the circuit.
4. How are components connected in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: Components in a parallel circuit are connected across the same two points, creating multiple paths for the current to flow.
5. What is the total resistance in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: The reciprocal of the total resistance in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
6. How does adding resistors affect the total resistance in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: Adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance of the circuit.
7. If one bulb in a parallel circuit goes out, what happens to the others?
- Answer: If one bulb in a parallel circuit goes out, the others remain lit because each branch is independent, and the current can still flow through the other branches.
8. How is voltage distributed in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: In a parallel circuit, each component has the same voltage as the power source. Voltage is constant across all branches.
9. What is the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a parallel circuit?
- Answer: In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across all components, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each branch. Ohm’s Law (I = V/R) applies to each component.
10. Why is a parallel circuit preferred for household wiring? – Answer: Parallel circuits are preferred for household wiring because each electrical device can operate independently, and the failure of one device does not affect the others.
11. Can components in a parallel circuit have different resistances? – Answer: Yes, components in a parallel circuit can have different resistances. The total resistance is calculated using the reciprocal formula.
12. What happens to the brightness of bulbs in a parallel circuit when more bulbs are added? – Answer: Adding more bulbs in a parallel circuit does not affect the brightness of existing bulbs. Each bulb receives the full voltage and operates independently.
13. How does the removal of one resistor affect the total resistance in a parallel circuit? – Answer: The removal of one resistor in a parallel circuit increases the total resistance of the circuit.
14. Why is a fuse not always necessary in parallel circuits? – Answer: In a parallel circuit, each component operates independently, so a failure in one component does not interrupt the circuit. Therefore, fuses are not always necessary.
15. Can a parallel circuit contain only one component? – Answer: Yes, a parallel circuit can contain only one component, such as a single resistor or a single bulb.
16. How does the resistance affect the current flow in a parallel circuit? – Answer: As resistance increases in a parallel circuit, the current flowing through that particular branch decreases, but the total current remains constant.
17. Why does the failure of one component not affect the operation of other components in a parallel circuit? – Answer: The failure of one component in a parallel circuit does not affect others because each component has its own branch, and the current can still flow through unaffected branches.
18. In a parallel circuit, what happens to the total resistance if resistors are connected in series instead? – Answer: Connecting resistors in series in a parallel circuit increases the total resistance of the circuit.
19. How does the total resistance in a parallel circuit compare to the individual resistances? – Answer: The total resistance in a parallel circuit is less than the smallest individual resistance.
20. Why is it important to use components with the same voltage ratings in a parallel circuit? – Answer: Using components with different voltage ratings can lead to uneven voltage distribution, potential damage, or failure of components in a parallel circuit.
21. Can a short circuit occur in a parallel circuit? – Answer: Yes, a short circuit can occur in a parallel circuit if there is an unintended low-resistance pathway that bypasses one or more components.
22. How does the addition of a resistor affect the brightness of bulbs in a parallel circuit? – Answer: Adding a resistor in parallel does not affect the brightness of bulbs. Each bulb receives the full voltage and operates independently.
23. Why is it essential to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit before connecting it to a power source? – Answer: Calculating the total resistance helps ensure that the circuit operates within safe current limits and prevents damage to components.
24. Can a parallel circuit have both resistive and non-resistive components? – Answer: Yes, a parallel circuit can have a combination of resistive and non-resistive components such as bulbs, resistors, and other devices.
25. How does the parallel circuit concept apply to real-life applications, such as household wiring? – Answer: Household wiring is often done in parallel, allowing multiple devices to operate independently on the same power source. The failure of one device does not affect others.

