1. What is acid rain?
- Answer: Acid rain is precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail, with an unusually low pH, primarily caused by the presence of pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) in the atmosphere.
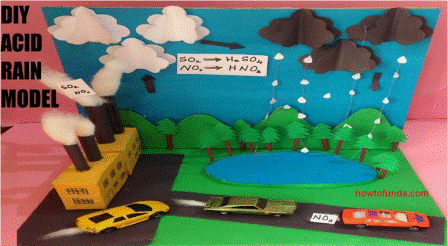
2. What are the main sources of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides causing acid rain?
- Answer: The main sources are burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) in power plants, industrial processes, and vehicle emissions.
3. How does acid rain form?
- Answer: Acid rain forms when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides released into the atmosphere undergo chemical transformations, creating sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃), which then mix with precipitation.
4. What is the pH range of acid rain?
- Answer: The pH of acid rain is below 5.6, with the range varying from mildly acidic to highly acidic.
5. How does acid rain affect aquatic ecosystems?
- Answer: Acid rain can lead to water acidification, harming fish and other aquatic life by affecting reproduction, growth, and survival.
6. What impact does acid rain have on soil?
- Answer: Acid rain leaches essential nutrients like calcium and magnesium from the soil, negatively impacting soil fertility and plant health.
7. How does acid rain affect forests?
- Answer: Acid rain can directly damage trees and harm forest ecosystems by leaching nutrients from leaves and needles.
8. Can acid rain damage buildings and monuments?
- Answer: Yes, acid rain can accelerate the decay of buildings, statues, and monuments made of limestone or marble by reacting with the materials.
9. What role does limestone play in mitigating the effects of acid rain?
- Answer: Limestone can act as a buffer, neutralizing acids and helping to mitigate the impact of acid rain on aquatic ecosystems and soil.
10. How does acid rain affect human health?
Answer: While acid rain itself is not directly harmful to human health, the pollutants that cause acid rain contribute to air pollution, impacting respiratory health.
11. Which areas are most affected by acid rain?
Answer: Areas with high industrial activities and dense transportation networks are often most affected by acid rain. Regions downwind from industrial areas may experience more severe effects.
12. How can acid rain be mitigated?
Answer: Mitigation strategies include reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, transitioning to cleaner energy sources, and enforcing environmental regulations.
13. Does acid rain affect drinking water?
Answer: Acid rain can impact the quality of drinking water sources, particularly in areas with vulnerable water supplies.
14. How does acid rain influence soil productivity in agriculture?
Answer: Acid rain can deplete soil nutrients, impacting soil fertility and reducing the productivity of agricultural lands.
15. Can acid rain affect air quality?
Answer: Yes, the pollutants causing acid rain contribute to air pollution, influencing overall air quality and impacting human health.
16. Is acid rain a local or a global issue?
Answer: Acid rain can be both a local and a global issue, depending on the sources of pollution and atmospheric conditions.
17. How does acid rain impact cultural heritage?
Answer: Acid rain poses a threat to cultural heritage by accelerating the decay of historical structures and monuments.
18. Are there natural sources of acid rain?
Answer: While there are natural sources of acidity in rain, acid rain as a result of human-induced pollutants is a significant concern.
19. How can individuals contribute to reducing acid rain?
Answer: Individuals can contribute by reducing energy consumption, supporting clean energy initiatives, and promoting responsible environmental practices.
20. Can acid rain be completely eliminated?
Answer: While complete elimination may be challenging, significant reductions in emissions and responsible environmental practices can substantially mitigate the impact of acid rain.
21. Does acid rain have a seasonality?
Answer: Acid rain does not have a specific seasonality; it can occur throughout the year depending on the prevailing atmospheric conditions.
22. What is the impact of acid rain on biodiversity?
Answer: Acid rain can negatively impact biodiversity by affecting the health and survival of various plant and animal species in affected ecosystems.
23. How does acid rain influence the pH of lakes and rivers?
Answer: Acid rain can lower the pH of lakes and rivers, leading to water acidification and impacting the aquatic life within these ecosystems.
24. What are the long-term effects of acid rain on ecosystems?
Answer: Long-term effects include changes in soil composition, damage to vegetation, and alterations to aquatic ecosystems that can persist for an extended period.
25. Are there international efforts to address acid rain?
Answer: Yes, international agreements and initiatives exist to address acid rain, emphasizing cooperation among nations to reduce emissions and protect the environment.

